

【Member News】Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology and Nanjing Electronic Devices Institute Have Collaborated to Achieve the First Preparation of Diamond-Based Gallium Oxide Heterojunction Integrated Materials and Devices
日期:2024-12-19阅读:1083
The Heterogeneous Integration XOI Team of Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology and the Ultra-Wide Bandgap Semiconductor Research Team of Nanjing Electronic Devices Institute have made a breakthrough in the field of Diamond-based heterogeneous integration materials and devices. The research results were presented in the form of an oral presentation "First Demonstration of Wafer-level Arrayed β-Ga2O3 Thin Films and MOSFETs on Dec 9 at the 70th International Congress on Electronic Devices (IEDM 2024) Diamond by Transfer Printing Technology ". Doctoral student Zhao Tiancheng, Senior Engineer Yu Xinxin of Nanjing Electronic Devices Institute and Assistant Researcher Xu Wenhui are co-first authors of this paper, assistant researcher Xu Wenhui, Researcher Ou Xin, Researcher Li Zhonghui of Nanjing Electronic Devices Institute are co-corresponding authors, and Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology is the first completion unit.
In wide/ultra-wide band gap semiconductor materials, Gallium Oxide has the lowest thermal conductivity (0.1-0.27W /m·K), which is less than 1/5 of Silicon materials, which makes Gallium Oxide devices face serious reliability problems such as self-heating effect and short life under high power conditions. Diamond is the material with the highest known thermal conductivity in nature, and it is an ideal heat sink substrate material for high-power and RF devices. The application of Diamond for heterogeneous integration is becoming an important research direction for thermal management of high-power devices, as shown in Figure 1. however, power and RF semiconductor materials such as Diamond and Gallium Oxide have high lattice mismatch. And the wafer morphology and surface smoothness of Diamond are poor, which make it a great challenge to realize diamond-based heterogeneous integration materials by direct epitaxial growth and wafer bonding.
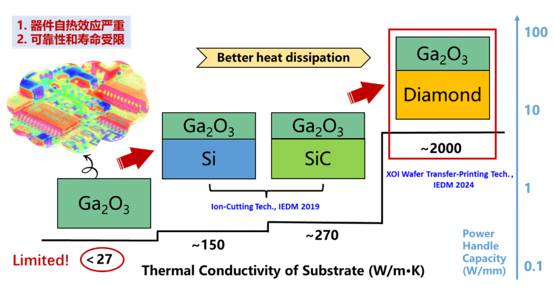
FIG. 1 Development trend of Gallium Oxide high thermal conductivity heterogeneous integration technology
The research team of Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology innovated and developed XOI wafer transfer technology, and took the lead in the world in realizing the heterogeneous integration of array Gallium Oxide single crystal film with 1-inch Diamond substrate, as shown in Figure 2. After transfer treatment, the Gallium Oxide single crystal film has a FWHM of 78 arcsec and surface roughness of 0.35 nm. The Diamond/Gallium Oxide interfacial transition layer thickness is less than 2 nm, and the interfacial thermal resistance is 21.7m2 ·K/GW, which is the optimal value reported so far. Based on this, the performance and heat dissipation capacity of the prepared RF device are significantly improved. The saturation current of the device in the open state is as high as 810 mA/mm, and the maximum oscillation frequency reaches 61 GHz before de-embedding, which is the highest value reported at present. At the same power, the maximum junction temperature of the device is reduced by 250℃ compared with the Gallium Oxide homogeneous device, the heat dissipation capacity is increased by 11 times, and the thermal resistance of the device is only 5.52W·mm/K, which greatly improves the performance and heat dissipation capacity of Gallium Oxide RF devices. This method not only has low cost and is not limited by wafer surface quality, but also is compatible with the transfer of other XOI heterogeneous integration films of different sizes and types to any substrate or even any bit direction.

Figure 2. (a) 1-inch Diamond-based array Gallium Oxide single crystal film and its preparation process; (b) Comparison of junction temperature and thermal resistance of Diamond-based Gallium Oxide and Gallium Oxide homogeneous film RF MOSFET devices
This work fully proves that wafer-grade diamond-based Gallium Oxide heterogeneous integration materials have excellent heat dissipation capability and RF application prospects, which is another new breakthrough after Silicon and Silicon Carbide based Gallium Oxide heterogeneous integration materials (IEDM 2019), and will further promote the development of high-performance Gallium Oxide devices, and provide a new paradigm for the preparation of Diamond-based heterogeneous integration materials. The research results have been supported by the Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research and Development Program and Shanghai Strategic Frontier Special Project.


