

【Domestic News】Institute of Nuclear Energy Safety Technology Has Made New Progress in the Development of Semiconductor Radiation Detectors for Ultra-Wide Bandgap Materials
日期:2025-01-10阅读:1258
Recently, the Institute of Nuclear Energy Safety Technology, in cooperation with Nanjing University, University of Science and Technology of China and other units, made a new progress in the development of semiconductor-based radiation detectors, and the relevant results were published in the IEEE Electron Device Letters journal.
The radiation detector is the "eye" of human understanding of the microscopic world, which can be used to observe and study nuclear radiation and microscopic particles, and plays an irreplaceable role in the fields of basic research, nuclear energy development and nuclear technology application. However, the detectors widely used at present have the problem of low sensitivity or insufficient environmental adaptability, which cannot meet the application requirements under high temperature and strong irradiation environmental conditions. The semiconductor-based radiation detectors based on wide band gap and ultra-wide band gap materials have many advantages, such as high temperature resistance, radiation resistance and easy integration, which is an important development direction of advanced radiation detection technology research and development in recent years. Based on semiconductor-based radiation detection technology of wide band gap and ultra-wide band gap materials, researchers of the Institute of Nuclear Energy Safety Technology optimized the design, preparation process and test scheme of the detector in view of the existing problems of the detector, greatly improved the performance index of the radiation detector, and achieved relevant research results.
A large area Nickel Oxide-Gallium Oxide (p-NiO/β-Ga2O3) device with low interfacial state density and leakage current level has been prepared, coupled with boron neutron conversion material, and obtained a intrinsic neutron detection efficiency of nearly 1%, completing the first experimental verification of the Ga2O3 based radiation detector for thermal neutron detection. It is a useful exploration for the development of neutron detection technology under extremely harsh environmental conditions.
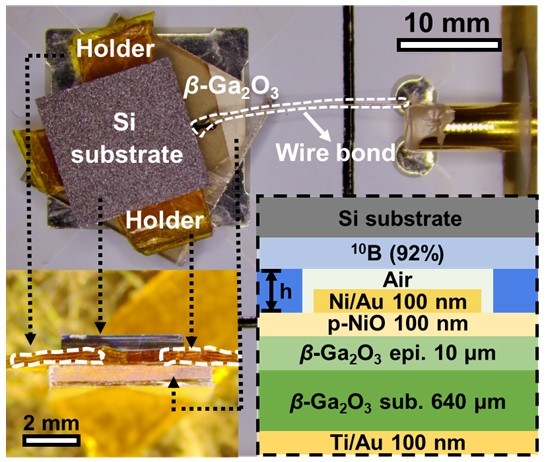
Fig-1 Ga2O3 device object, optical microscope photo and structure diagram
The above research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Collaborative Innovation Cultivation Fund of Hefei Comprehensive National Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and The Open Fund Project of Ministry of Education. Links to this article: https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2024.3522482


