

【International Papers】In-situ reflectance analysis of Si-doped β-Ga₂O₃ films grown by MOVPE: The influence of doping concentration and substrate conductivity
日期:2025-03-21阅读:710
Researchers from the Leibniz Institute for Crystal Growth (IKZ), Germany have published a dissertation titled " In-situ reflectance analysis of Si-doped β-Ga₂O₃ films grown by MOVPE: The influence of doping concentration and substrate conductivity" in Journal of Applied Physics.
Project Support
This research was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (Grant No. 16ES1084K), the German Research Foundation (DFG) (Project No. PO-2659/1-2), and the European Regional Development Fund (EFRE) (Grant No. 1.8/15).
Background
β-Ga₂O₃ has garnered significant attention due to its ultra-wide bandgap (~4.8 eV) and high breakdown field (up to 8 MV/cm). Metalorganic vapor-phase epitaxy (MOVPE) is a widely used thin-film growth technique known for its uniform deposition and scalability for large-scale production. To optimize film quality and doping uniformity, in-situ monitoring plays a crucial role during the growth process. Traditional thin-film characterization methods typically require post-growth analysis, which may lead to undetected issues during growth, affecting film quality and device performance. In contrast, in-situ monitoring allows real-time acquisition of key parameters such as film thickness, growth rate, surface morphology, and doping concentration. This real-time feedback enables researchers to adjust growth conditions promptly, optimizing film quality and uniformity.
In the homoepitaxial growth of β-Ga₂O₃, traditional ellipsometry struggles to resolve meaningful signals due to the similar optical properties of the film and substrate. However, high-sensitivity reflectance spectroscopy can overcome this limitation by analyzing interference patterns, providing deep insights into film growth dynamics and doping effects. Therefore, in-situ reflectance measurement holds significant value in the growth of β-Ga₂O₃ films.
Abstract
This study focuses on using in-situ reflectance measurement to monitor the dynamic changes of Si-doped β-Ga₂O₃ films during MOVPE growth, particularly the effects of doping concentration and substrate conductivity on the optical and electrical properties of the films. Below are the key findings:
1. Interference Oscillation Patterns in Reflectance Spectra
During film growth, researchers used the in-situ reflectance measurement system (Laytec EpiNet) to monitor reflectance spectra at different wavelengths (405 nm, 633 nm, 950 nm). The study revealed distinct interference oscillation patterns in the reflectance spectra, closely related to the film's growth rate and doping concentration.
● Mechanism of Interference Oscillations: These oscillations arise from the refractive index contrast between the film and substrate, known as Fabry-Pérot interference. Multiple reflections of light between the film and substrate create interference effects, forming oscillation patterns.
● Oscillation Period and Growth Rate: The period of the oscillations is directly related to the film's growth rate. By analyzing the period, researchers can estimate the growth rate in real time.
● Oscillation Amplitude and Doping Concentration: The amplitude of the oscillations correlates with the film's doping concentration. As doping increases, the refractive index changes, leading to larger oscillation amplitudes.
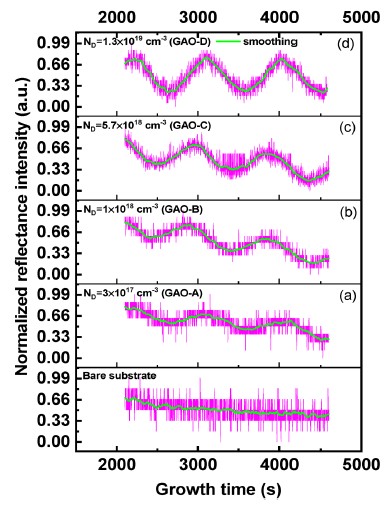
Figure 1: Reflectance signals of β-Ga₂O₃ films with different doping concentrations at 950 nm.
2. Effect of Doping Concentration on Refractive Index
The study further explored the impact of Si doping concentration on the refractive index of β-Ga₂O₃ films. Using the Drude model, researchers quantified the doping-induced changes in refractive index.
● Drude Model Application: The Drude model describes how free carriers (e.g., electrons) influence the optical properties of materials. At high doping concentrations, increased free carrier density alters the material's dielectric constant and refractive index.
● Refractive Index Changes: The study found that as Si doping concentration increases, the film's refractive index decreases significantly. This effect is more pronounced at longer wavelengths (e.g., 950 nm) due to stronger free carrier absorption.
3. Effect of Substrate Conductivity
The study also investigated the influence of substrate conductivity on film growth and optical properties. Two types of substrates were used: semi-insulating (Mg-doped) and conductive (Si-doped).
● Semi-insulating vs. Conductive Substrates: Films grown on semi-insulating substrates showed less pronounced interference oscillations due to smaller refractive index contrasts. In contrast, films grown on conductive substrates exhibited stronger oscillations due to larger refractive index differences.
● Unintentionally Doped (UID) Films: The study compared UID films grown on semi-insulating and conductive substrates. Results showed that only films on conductive substrates displayed clear interference oscillations, further demonstrating the impact of substrate conductivity on optical properties.
4. Burstein-Moss Effect and Plasmonic Effect
The study analyzed the contributions of the Burstein-Moss effect and plasmonic effect to refractive index changes.
● Burstein-Moss Effect: Increased doping fills the conduction band, shifting the absorption edge to higher energies (Burstein-Moss shift) and causing minor refractive index changes. However, in β-Ga₂O₃, the effect is relatively small due to the material's large electron effective mass.
● Plasmonic Effect: The collective oscillation of free carriers (plasmonic effect) significantly impacts refractive index at high doping concentrations. Using the Drude model, researchers calculated the plasmonic effect's contribution, finding it dominant at longer wavelengths.
5. Theoretical Simulation and Experimental Validation
To validate the experimental results, researchers used the Transfer Matrix Method (TMM) to simulate reflectance spectra. By comparing experimental data with simulations, they accurately estimated the film's refractive index changes and thickness, further confirming the reliability of in-situ reflectance measurement.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the effectiveness of in-situ reflectance measurement in monitoring the dynamic changes of Si-doped β-Ga₂O₃ films during MOVPE growth. The interference oscillation patterns in reflectance spectra are closely tied to the film's growth rate and doping concentration, while substrate conductivity significantly influences optical properties. Using the Drude model and TMM, researchers quantified doping-induced refractive index changes and validated the reliability of in-situ reflectance measurement. This research provides critical theoretical and technical support for optimizing β-Ga₂O₃ film growth and device applications.


