

【Device Papers】Highly transparent β-Ga₂O₃/NiO heterojunction-based photovoltaic solar-blind photo-communication window
日期:2025-04-27阅读:530
Researchers from the Multidisciplinary Core Institute for Future Energies (MCIFE) have published a dissertation titled "Highly transparent β-Ga2O3/NiO heterojunction-based photovoltaic solar-blind photo-communication window" in Sensors and Actuators A: Physical.
Abstract
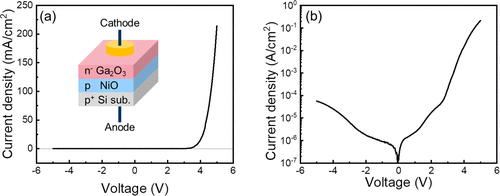
Developing high-performance, deep-ultraviolet (DUV) devices that are invisible to the human eye is imperative for advancing next-generation transparent electronics. This work introduces a novel photovoltaic-integrated transparent photodetector (TPD) based on a Ga2O3/NiO heterojunction. The wide bandgap of n-Ga2O3 (∼4.5 eV) allows the heterojunction to effectively absorb DUV photons while remaining insensitive to longer wavelength photons. The p-type NiO provides a well-matched bandgap and suitable work function for fabricating a type II heterojunction, which enhances the efficient extraction of charge carriers at the interface. The valence band offset and a large built-in potential at the heterointerface provide advantageous energetics for separating and migrating photogenerated excitons, making it particularly useful for self-powered, solar-blind UV photodetection. Transparent silver nanowires electrodes are employed to ensure the device remains completely invisible to the human eye. The self-powered functionality eliminates the need for an external bias, simplifying device integration. The fabricated Ga2O3/NiO heterojunction-based transparent photovoltaic device exhibits an open-circuit value of 639 mV under DUV illumination, with an average visible transparency of 65 %. The TPD exhibits a fast photoresponse with a response time of 30 µs. Furthermore, we demonstrate an online real-time photo-communication monitoring application based on this device, as well as a wide-field-of-view for solar-blind photo-communication. The device's transparency and omnidirectional behavior pave the way for its use in various optoelectronic applications, including artificial intelligence eyes, wide-field-of-view cameras and antennas, solar-blind imaging, and more.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2025.116553


