【Member News】Advanced Science by Wang Gang of Sun Yat-sen University: Application of Wide Band-Gap Ga₂O₃ Semicond
日期:2023-03-06阅读:843
Background
With the rise and popularization of 5G technology, more and more attention has been paid to how to use different communication frequency bands reasonably and efficiently. At present, there are more than 30 communication frequency bands available for use, and the number will continue to grow with the development of wireless communication technology. Therefore, RF filters play an increasingly important role in wireless communication technology. The demand for filters in the RF front-end of mobile phones alone is more than 10 billion per year. Therefore, it is particularly important to develop high-performance RF filters. At present, filters used in RF front-end are mainly made of piezoelectric materials: in low frequency band (<2 GHz), mainstream commercial RF filters mainly use surface acoustic wave devices (SAW) based on piezoelectric crystal LiNbO3 or LiTaO3; In the high-frequency band (>2 GHz), thin film bulk acoustic wave devices (FBARs) based on piezoelectric semiconductor AlN are mainly used.
Piezoelectric semiconductor materials used in RF filters need to have high intrinsic resistivity (i.e. wide band gap) and high piezoelectric coefficient; The former is helpful to improve the output power and quality factor of the device, while the latter is helpful to increase the bandwidth of the filter. As the mainstream semiconductor material of 5G RF filter at present, AlN has enough wide band gap (6.2 eV); However, the piezoelectric constant of AlN is only d33=1-5 pm/V, which means that the electro-mechanical coupling factor of AlN material is small, and the corresponding filter bandwidth is also small. Therefore, finding new piezoelectric semiconductor materials with higher performance is one of the core topics in the research field of RF devices. Recently, the research team of Sun Yat-sen University has made important progress in the research field of wide band gap piezoelectric semiconductor materials. The paper entitled《 ε- Ga2O3: an Emerging Wide Bandgap Piezoelectric Semiconductor for Application in Radio Frequency Resonators》, is published in the international journal Advanced Science. Associate professor Chen Zimin of Sun Yat-sen University is the first author of the paper, and associate professors Lu Xing and Wang Gang of Sun Yat-sen University are the corresponding authors of the paper.
Research results
In recent years, new gallium oxide (Ga2O3) semiconductor materials have attracted extensive attention in the field of semiconductor research due to their advantages of wide band gap (4.9 eV) and high breakdown electric field (8 MV/cm). Ga2O3 has α、β、γ、δ and ε five different phases, of which ε- Ga2O3 (also known as κ- Ga2O3) is the second stable phase of gallium oxide, and ε- Ga2O3 can only be obtained by heteroepitaxial growth. Theoretical research points out that ε- Ga2O3 has strong piezoelectric polarization effect, but due to the preparation technology of ε-Ga2O3 thin film is still immature, there is still a lack of experimental verification and application research of ε- Ga2O3’s piezoelectric effect.
The research team of Sun Yat-sen University can grow heteroepitaxy ε- Ga2O3 thin film on silicon, sapphire, silicon carbide and other substrates by using the metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) method; The film has the characteristics of low residual stress and high crystal quality. By using piezoelectric atomic force microscope (PFM) the piezoelectric coefficient of ε-Ga2O3 film along the c-axis direction is d33=10.8-11.2 pm/V (Fig. 1), which is significantly higher than that of AlN (d33=1-5pm/V). The research group adopted semiconductor micro-machining process, and realized the first SAW RF resonator based on ε-Ga2O3 thin film (Fig. 2), which has significant piezoelectric resonance (including Rayleigh mode and Sezawa mode) in the range of 1-3 GHz. It further verifies that ε-Ga2O3 thin film material has great potential in application of 5G RF band.
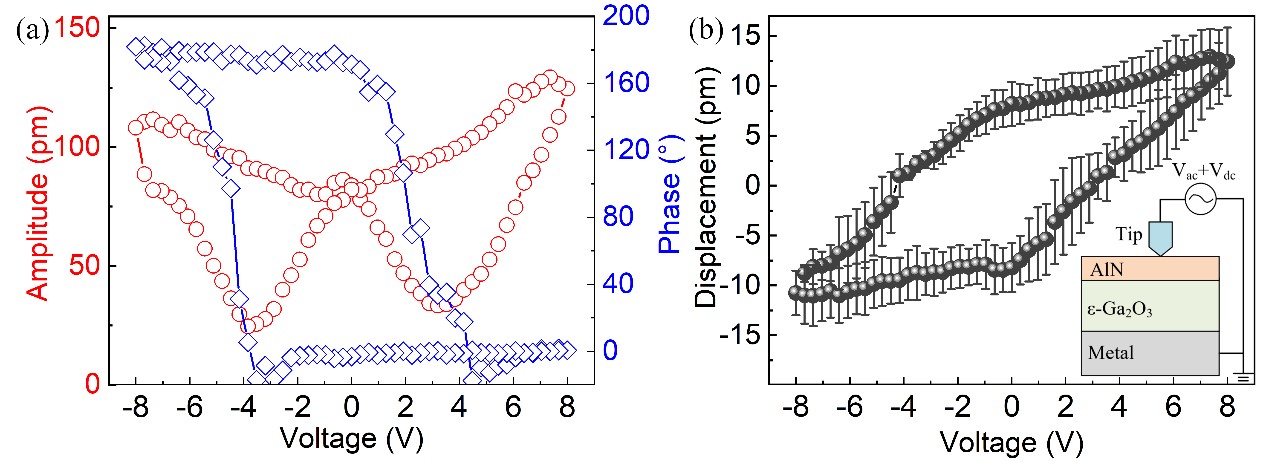
Figure 1: PFM Measurement of Piezoelectric Effect of ε- Ga2O3 Thin Films
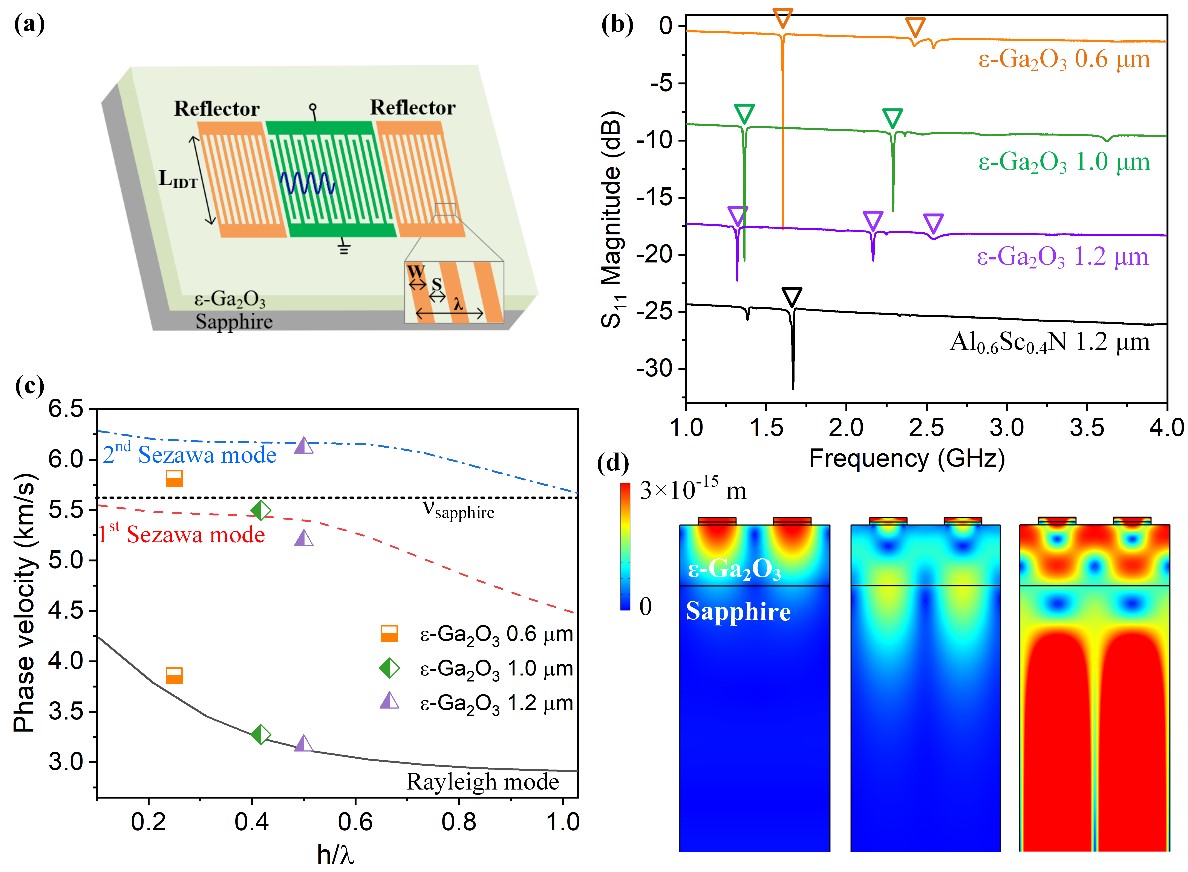
Figure 2: Operating Characteristics of SAW RF Resonator based on ε-Ga2O3 Thin Film
Summary and prospect
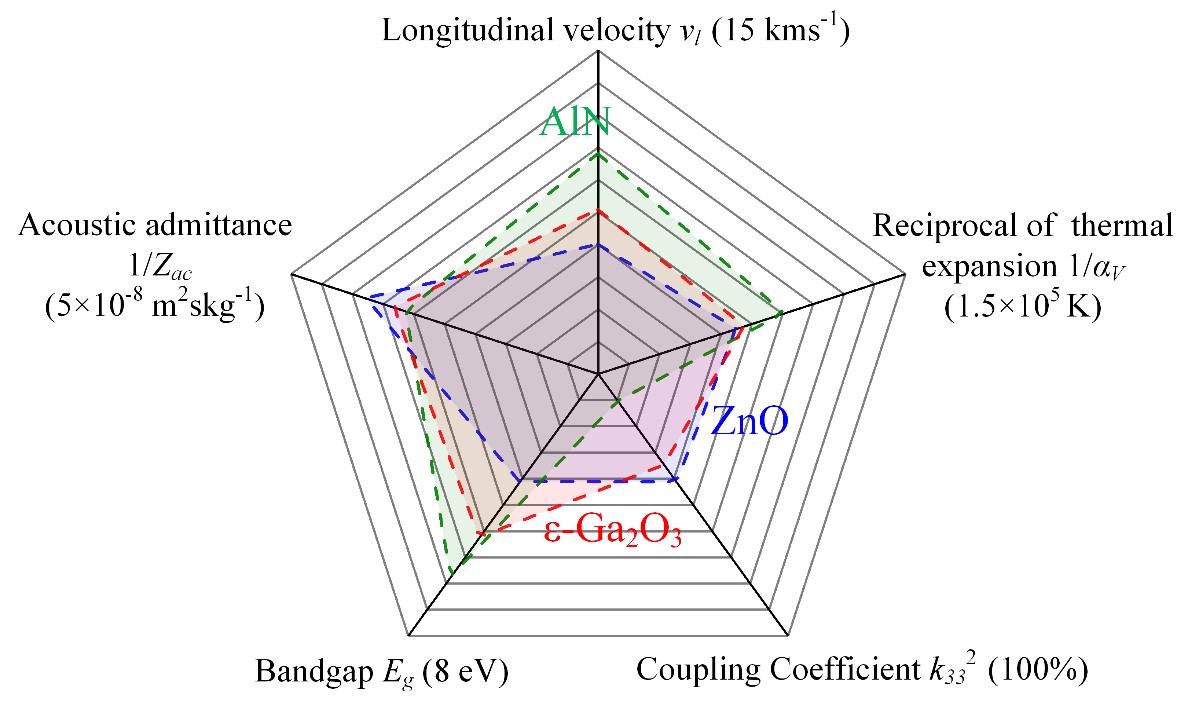
The piezoelectric coefficient of ε-Ga2O3 is d33=10.8-11.2 pm/V. Theoretically, the electro-mechanical coupling coefficient of the FBAR RF filter based on ε-Ga2O3 film can be 4 times of that of AlN. ε- Ga2O3 has outstanding material comprehensive properties (Figure 3), which can solve the shortcomings of AlN filters in bandwidth, and has great application potential in 5G RF technology. (Article link https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202203927 )