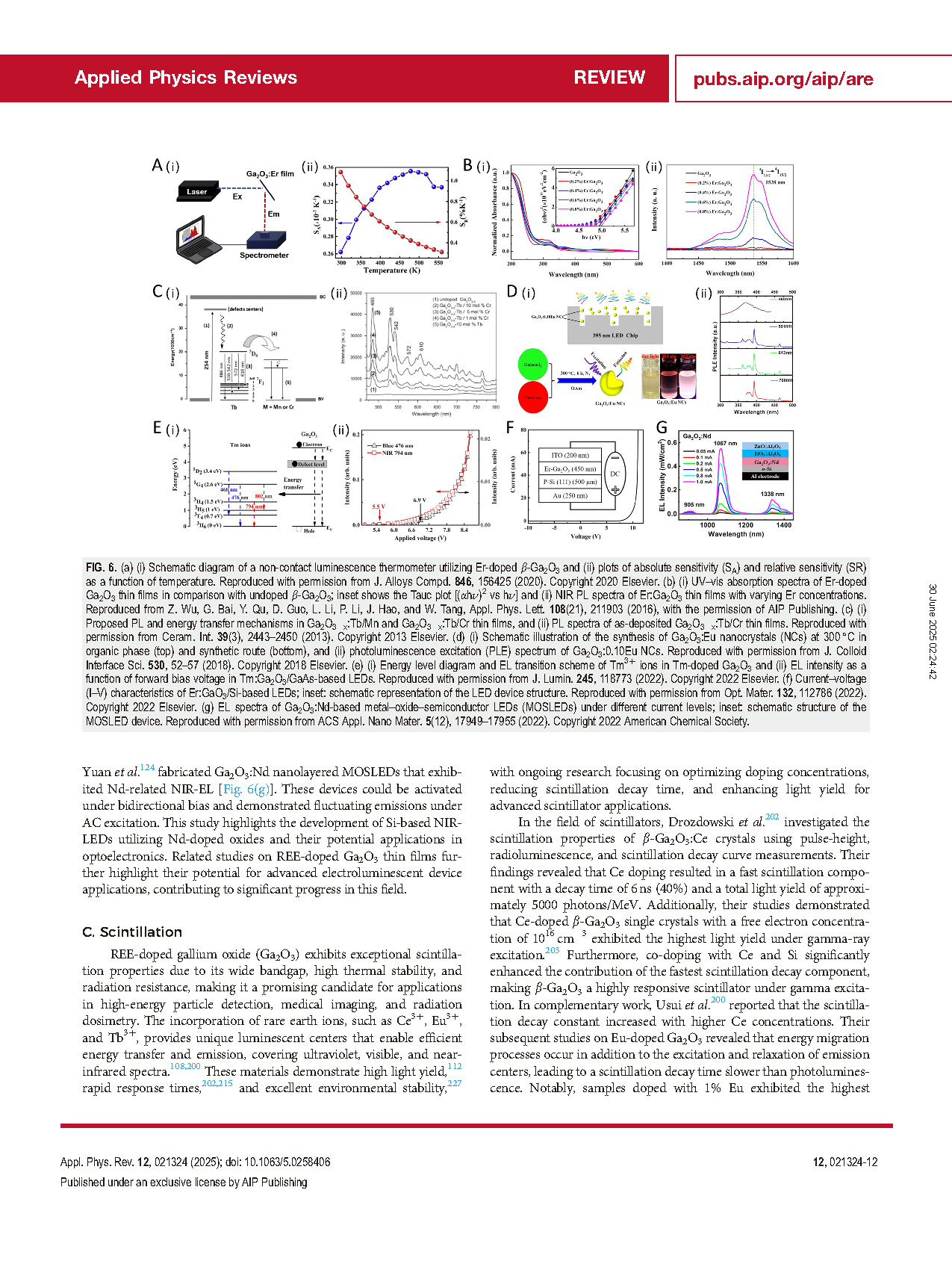
【Member Papers】Rare earth element applications in Ga₂O₃: Luminescence and scintillation
日期:2025-07-10阅读:415
Researchers from the The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou) have published a dissertation titled "Rare earth element applications in Ga2O3: Luminescence and scintillation" in Applied Physics Reviews.
Project Support
The work was supported by C. K. Tan start-up fund from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou), Bureau of Science and Information Technology of Guangzhou Municipality j Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Project (Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan) (Nos. 2023A03J0003, 2023A03J0013, 2023A04J0310, and 2023A03J0152), Department of Education of Guangdong Province (DEGP) (No. 2024ZDZX1005), the State Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs China (No. Y20240005).
Background
Gallium oxide (Ga2O3), an emerging ultra-wide bandgap semiconductor with a bandgap of approximately 4.85 eV, has garnered attention for its potential in next-generation high-power electronic devices due to its ultrawide bandgap, high critical field, high thermal and chemical stability, and impressive optical properties. Extensive research has focused on its use in high-energy radiation detection, ultraviolet (UV) photodetectors, light-emitting diodes (LEDs), and photonic devices, attributed to its strong performance in photoluminescence (PL), electroluminescence (EL), scintillation, and photocatalysis. Among its isomers, β-Ga2O3 is the most stable, with a bandgap between 4.5 and 4.9 eV, facilitating effective photoemission from the UV to the visible range. Additionally, β-Ga2O3 exhibits high optical transparency and strong dielectric strength in the deep UV range, making it suitable for transparent conducting oxides. However, low intrinsic carrier mobility and luminescence efficiency limit its optical and electrical properties. To address these limitations, doping with rare earth element (REE) has been proposed, offering a promising strategy to enhance these properties and expand the functional potential of Ga2O3-based devices.
Abstract
Gallium oxide (Ga2O3), with its ultrawide bandgap, exceptional stability, and good optical properties, has demonstrated significant potential in high-power electronic devices, photodetectors, and high-energy radiation detection. However, its low carrier mobility and limited luminescence efficiency constrain its performance. Rare earth element (REE) doping, including europium (Eu), cerium (Ce), erbium (Er), and others, introduces localized states within the Ga2O3 bandgap, enhancing luminescence, scintillation, and catalytic activity, while enabling multi-functional applications through co-doping strategies. Therefore, the paper reviews the commonly employed REE-doped Ga2O3 synthesis methods (wet chemical methods, ALD, PLD, MBE, et al.) and the roles of REE dopants (Eu, Er, Tb, Ce, et al.) in luminescent and scintillation performance. Furthermore, the review highlights recent advances in REE-doped Ga2O3 for photoluminescence, electroluminescence, scintillation, photonic devices, and catalysis. These insights will guide breakthroughs in optoelectronics, radiation detection, and biomedicine applications.

FIG. 1. Rare earth element applications in Ga2O3: luminescence and scintillation.
DOI:
doi.org/10.1063/5.0258406