【Member Papers】High Performance α-Ga₂O₃ Deep Ultraviolet Photodetector Grown by Mist-CVD
日期:2025-11-07阅读:12
Researchers from the Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications have published a dissertation titled "High Performance α-Ga2O3 Deep Ultraviolet Photodetector Grown by Mist-CVD" in IEEE Photonics Technology Letters.
Project Support
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62304113, 62204126, 62334003 and U23B2042.
Background
Deep-ultraviolet (DUV) photodetectors are critical for applications such as flame detection, space communication, missile warning, and environmental monitoring, requiring solar-blind operation. Among wide-bandgap semiconductors, metastable α-Ga₂O₃ is a promising candidate due to its ultra-wide bandgap (~5.2 eV), excellent thermal stability, and high breakdown field. Mist chemical vapor deposition (mist-CVD) enables low-cost, scalable growth of high-quality α-Ga₂O₃ thin films, yet previous devices often suffer from low responsivity or long response times due to material and interface defects. Recent studies demonstrate that mist-CVD-grown α-Ga₂O₃ metal–semiconductor–metal photodetectors can achieve kilovolt-ampere-per-watt-level responsivity with millisecond-scale response times, highlighting the potential of this approach for high-performance DUV photodetectors.
Abstract
In this letter, we report the fabrication and characterization of a metal–semiconductor–metal (MSM) deep-ultraviolet (DUV) photodetector based on α-Ga2O3 thin films grown by mist chemical vapor deposition (mist-CVD). The α-Ga2O3 films exhibit excellent crystallinity and surface uniformity, enabling the realization of high-performance DUV photodetectors. The fabricated device achieves an ultra-high responsivity exceeding 1000 A/W at 210 nm, an ultra-low dark current of 0.12 pA at 5 V, and a high UV-to-visible rejection ratio of ~105. In addition, a temporal response with a decay time of millisecond scale is observed. These results demonstrate the viability of mist-CVD-grown α-Ga2O3 for scalable and cost-effective fabrication of next-generation DUV optoelectronic devices.
Conclusion
In summary, a high-performance DUV PD based on α-Ga2O3 thin films grown by mist-CVD has been demonstrated. The epitaxial α-Ga2O3 film exhibits excellent crystalline quality, wide optical bandgap (5.28 eV), and smooth surface morphology. The resulting MSM PD achieves a peak responsivity exceeding 1000 A/W at 210 nm, ultra-low dark current (~0.12 pA), a high UV-to-visible rejection ratio (~105), and decay times below 100 ms. The device also exhibits robust cycling stability, maintaining consistent performance across repeated switching. These results confirm that mist-CVD is a viable, scalable, and low-cost route for fabricating high-performance DUV PDs.

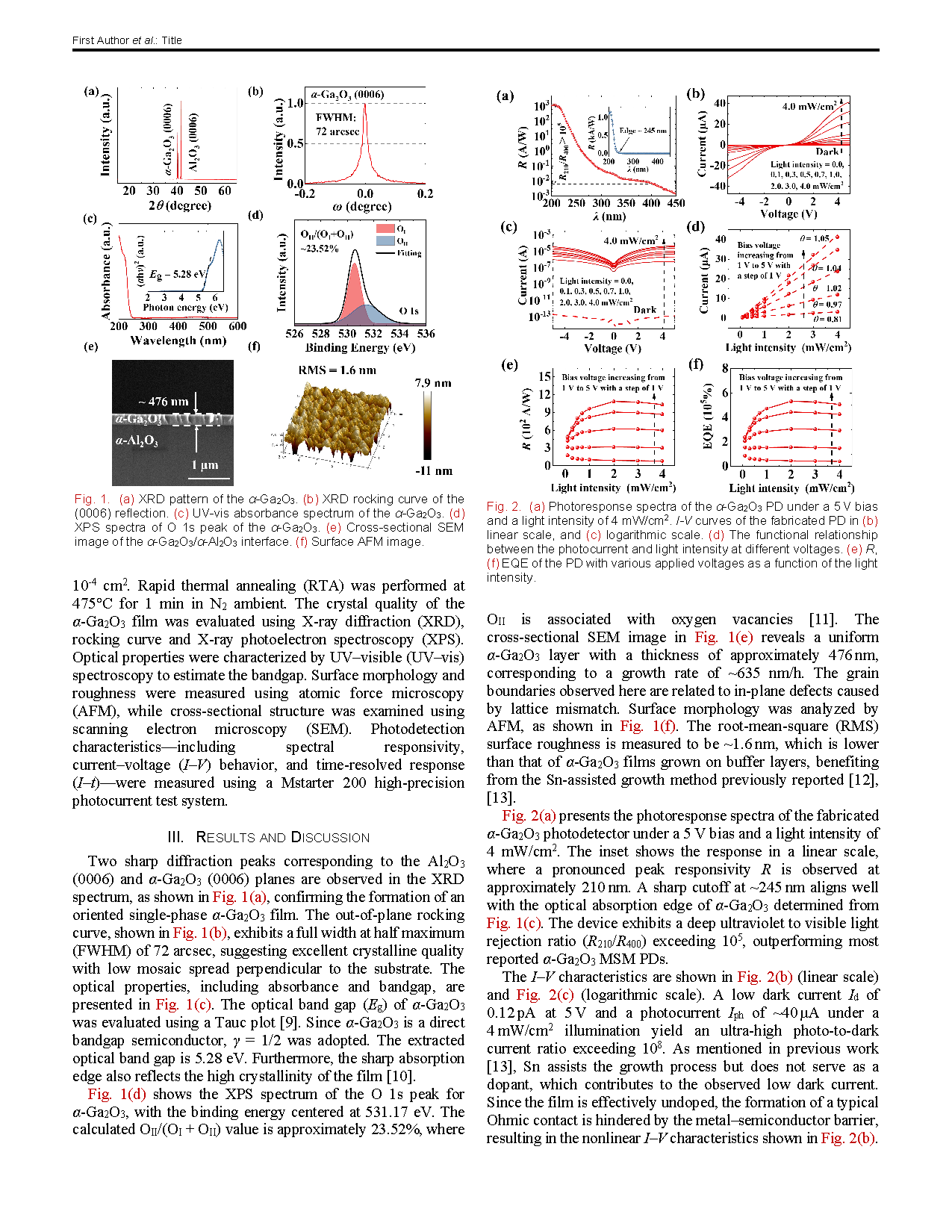
Fig. 1. (a) XRD pattern of the α-Ga2O3. (b) XRD rocking curve of the (0006) reflection. (c) UV-vis absorbance spectrum of the α-Ga2O3. (d) XPS spectra of O 1s peak of the α-Ga2O3. (e) Cross-sectional SEM image of the α-Ga2O3/α-Al2O3 interface. (f) Surface AFM image.
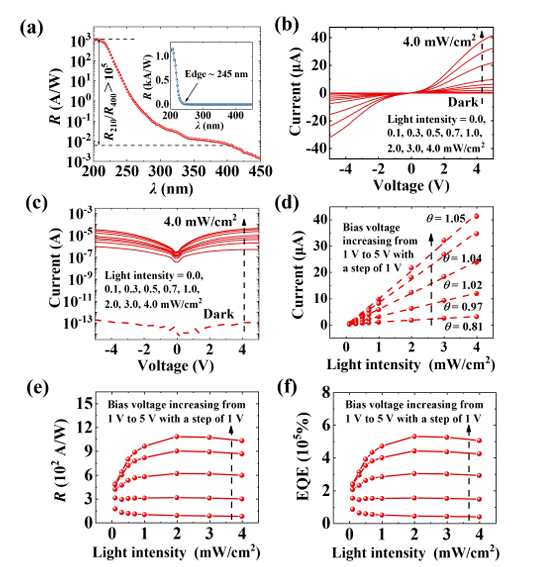
Fig. 2. (a) Photoresponse spectra of the α-Ga2O3 PD under a 5 V bias and a light intensity of 4 mW/cm2. I-V curves of the fabricated PD in (b) linear scale, and (c) logarithmic scale. (d) The functional relationship between the photocurrent and light intensity at different voltages. (e) R, (f) EQE of the PDwith various applied voltages as a function of the light intensity.
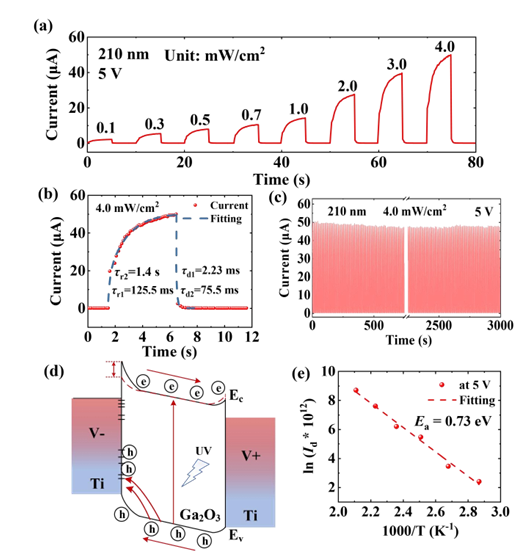
Fig. 3. (a) I-t curves of the fabricated PD under different light intensities. (b) The fitted curve of the single on/off cycle. (c) Measured switching characteristic of the DUV PD over 300 operational cycles. (d) Energy band conception diagram of the DUV PD. (e) Extraction of the activation energy of the dark current.
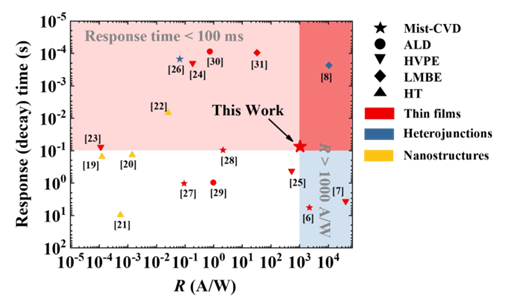
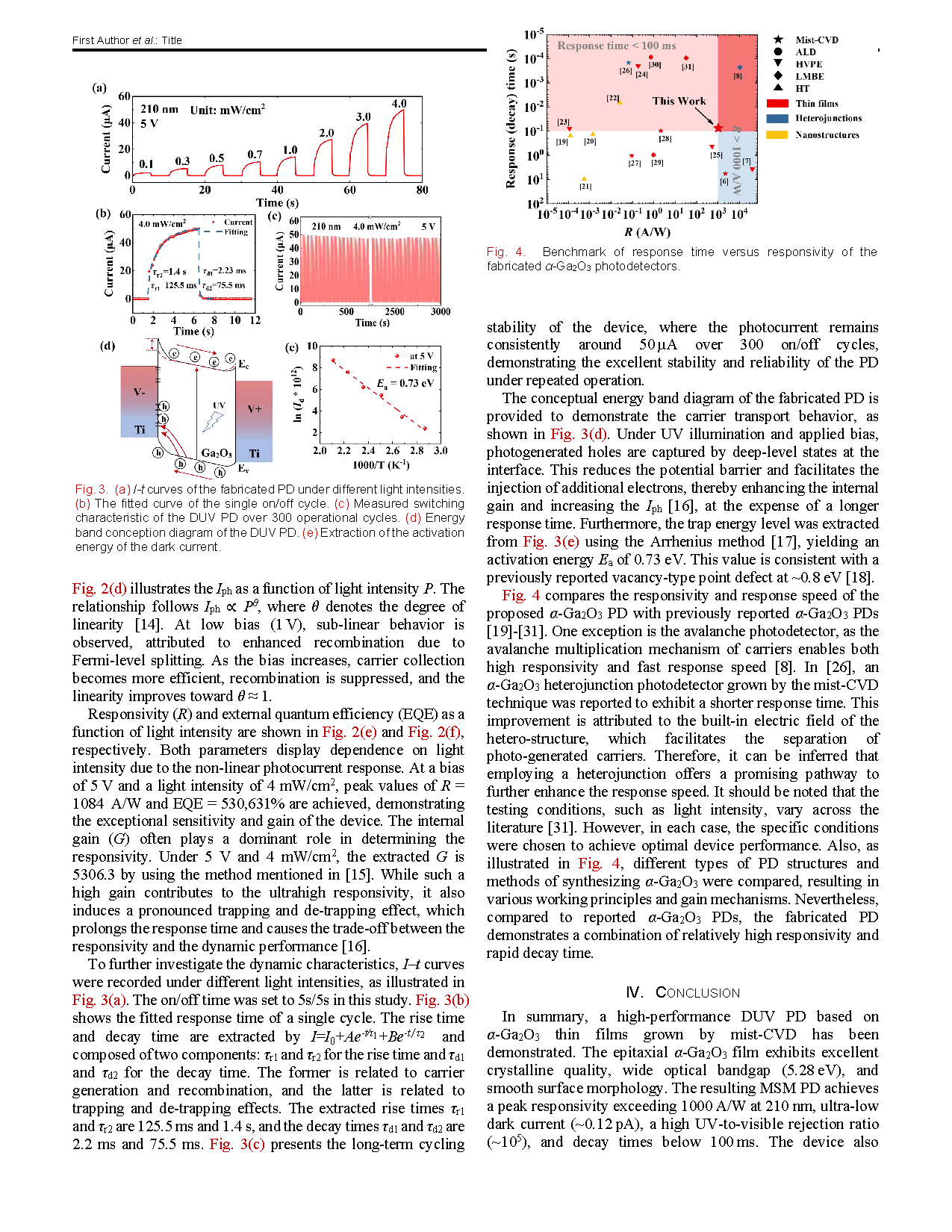
Fig. 4. Benchmark of response time versus responsivity of the fabricated α-Ga2O3 photodetectors.
DOI:
doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2025.3627605