

【Domestic News】A New Breakthrough Made by Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications in the Field of Gallium Oxide Based Solar-Blind Avalanche Detector!
日期:2023-03-14阅读:735
Recently, research group of Professor Zhen-Ping Wu , from the Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications College of Science, associated with research groups from NanKai University, Hong Kong Polytechnic University successfully developed the unipolar barrier type gallium oxide based solar blind avalanche photodetector via lattice and belt engineering control. The device performance breaks through the existing detective limit of solar blind ultraviolet detector, reaches the level of photomultiplier tube for commercial application, provides a new ideas for the development of high performance of solar blind avalanche detector. On January 26th ,2023, the relevant results were published in the international academic journal Nature Communications entitled "under the title of" Enhanced Gain and Detectivity of Unipolar Barrier Solar Blind Avalanche Photodetector via Lattice and Band Engineering ".

Qingyi Zhang, a doctoral candidate in the School of Science, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, is the first author of the article, and Professor Zhenping Wu is the co-corresponding author. The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation of China, the Special Fund for Basic Research Funds of Central Universities, and the Hong Kong Research Grant Agency.
For a long time, vacuum ultraviolet photoelectric multiplier tube is mostly used for high sensitive solar blind ultraviolet detection, but this sensor has the disadvantages of large size and high working voltage. In recent years, thanks to the basic physics research of wide-band semiconductor and the breakthrough of material preparation technology, new chances have been brought for the development of semiconductor ultraviolet detectors. The "2021 Research Frontier Heat Index" listed "solar-blind ultraviolet photoelectric detector based on Ga₂O₃" as one of the top ten frontier research hot spots in physics. How to further improve the device performance has become an important issue in the field of solar blind detection.
Based on the results of the previous Ga₂O₃/ ITO n-n avalanche detectors (ACS Nano, 2021, 15:16654), after constant exploration, the research group adjusted the barrier height by inserting a suitable broadband gap material (MgO), and successfully developed the n-Barrier-n unipolar barrier avalanche photodetector composed of the β-Ga₂O₃/ MgO / Nb: SrTiO₃ heterojunction. Its larger conduction band offset increases the reverse breakdown voltage and significantly suppresses the dark current. A very small valence band offset makes the flow of minority carriers at the heterojunction (see Figure 1). The device achieves an avalanche gain of up to 5.9x10⁵ and a specific detectivity of 2.33x10¹⁶ Jones, with excellent performance comparable to the current widely used commercial photomultiplier tubes (see Figure 2).

Figure 1. Performance comparison of n-B-n monopolar barrier heterostructures with n-n-type heterostructure avalanche detectors
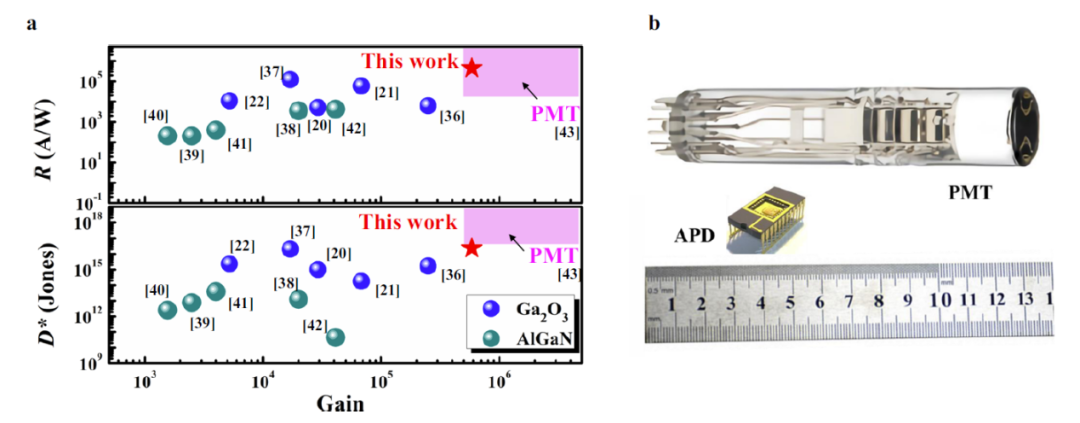
Figure 2. Ga₂O₃ / MgO / Nb: Performance comparison of STOn-B-n monopolar barrier avalanche detector with avalanche photodetector and photomultiplier tube in previous reports
This study creatively proposed a method to design n-B-n monopolar barrier Ga₂O₃ avalanche detector via lattice and band engineering, which significantly improved the device performance, meanwhile demonstrating the super potential of Ga₂O₃ in the next generation of high-voltage power devices and photoelectronic devices. This pioneering design also forges a new road for future Ga₂O₃ electronic devices with better performance.


