

【Device Papers】Ultrahigh Photocurrent in a Self-Powered Deep Ultraviolet Photodetector via P+/P/N-β-Ga₂O₃ Heterojunction and Patterned Top-Electrode Design
日期:2026-02-02阅读:17
Researchers from the Gachon University have published a dissertation titled "Ultrahigh Photocurrent in a Self-Powered Deep Ultraviolet Photodetector via P+/P/N-β-Ga2O3 Heterojunction and Patterned Top-Electrode Design" in ACS Applied Electronic Materials.
Abstract
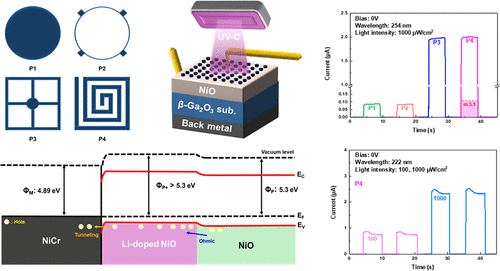
We achieved ultrahigh photocurrent in a deep-ultraviolet (DUV) photodetector with a Li-doped NiO (p+)/NiO (p)/β-Ga2O3 (n) heterojunction by designing a top electrode pattern and adding Li-doped NiO as a p+ layer. In DUV photodetectors, the pattern of the top electrode significantly influences device performance, including the electric field distribution, charge collection efficiency, and active area. Additionally, the incorporation of a p+ layer between the metal and p-type semiconductor can modify the band diagram, improve the quality of the ohmic contact, and enhance charge-transport characteristics. The device used an optimized electrode pattern with a Li-doped NiO layer as a p+ layer and demonstrated remarkable results at a wavelength of 254 nm and a light intensity of 1000 μW/cm2. It achieved a photocurrent of 2.0 μA at zero bias and 3.9 μA at 5 V. Furthermore, to evaluate the effectiveness of the device for arc detection, additional measurements were conducted at a wavelength of 222 nm, which lies within the peak wavelength range of arc emissions. The device recorded photocurrents of 2.4 μA at zero bias and 5.1 μA at 5 V, thus effectively demonstrating the capability to detect arcs. These results highlight the potential of adjusting previously unexplored parameters in NiO/β-Ga2O3 heterojunction-based DUV photodetectors to achieve significantly enhanced photocurrent levels.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.5c02534


