【International Papers】An Aerosol-Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition Route to Tin-Doped Gallium Oxide Thin Films with Optoelectronic Properties
日期:2024-11-15阅读:590
Researchers from the University College London have published a dissertation titled "An Aerosol-Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition Route to Tin-Doped Gallium Oxide Thin Films with Optoelectronic Properties" in ACS Applied Electronic Materials.
Abstract
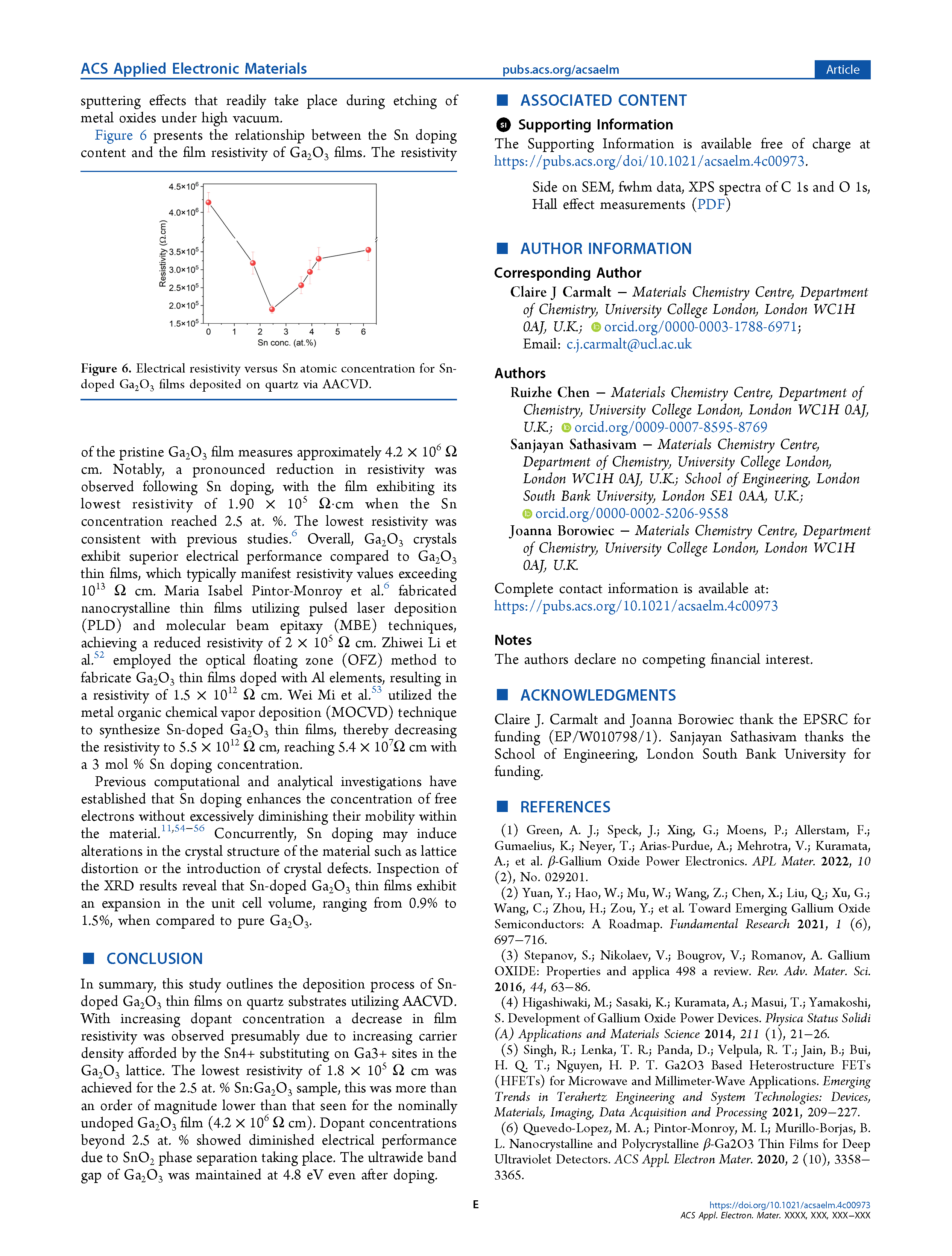
Gallium oxide is a wide-bandgap compound semiconductor material renowned for its diverse applications spanning gas sensors, liquid crystal displays, transparent electrodes, and ultraviolet detectors. This paper details the aerosol assisted chemical vapor deposition synthesis of tin doped gallium oxide thin films using gallium acetylacetonate and monobutyltin trichloride dissolved in methanol. It was observed that Sn doping resulted in a reduction in the transmittance of Ga2O3 films within the visible spectrum, while preserving the wide bandgap characteristics of 4.8 eV. Furthermore, Hall effect testing revealed a substantial decrease in the resistivity of Sn-doped Ga2O3 films, reducing it from 4.2 × 106 Ω cm to 2 × 105 Ω cm for the 2.5 at. % Sn:Ga2O3 compared to the nominally undoped Ga2O3.
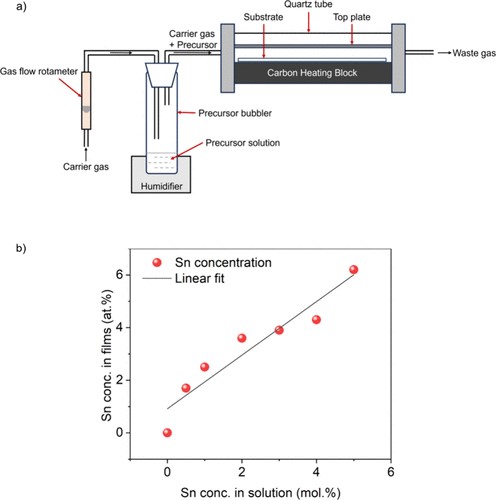
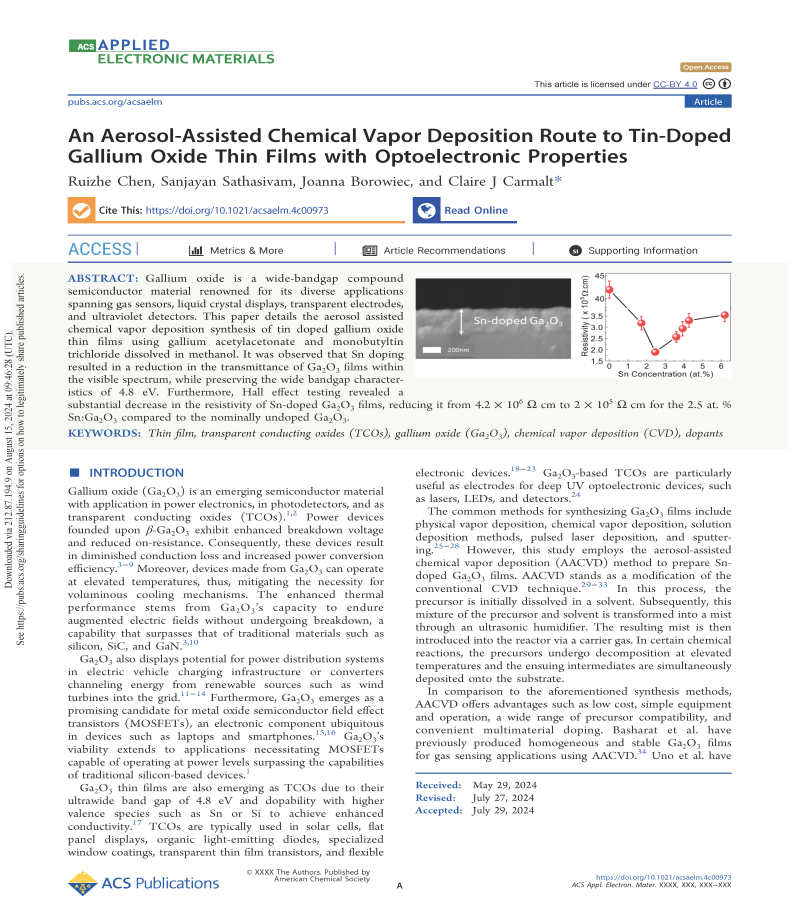
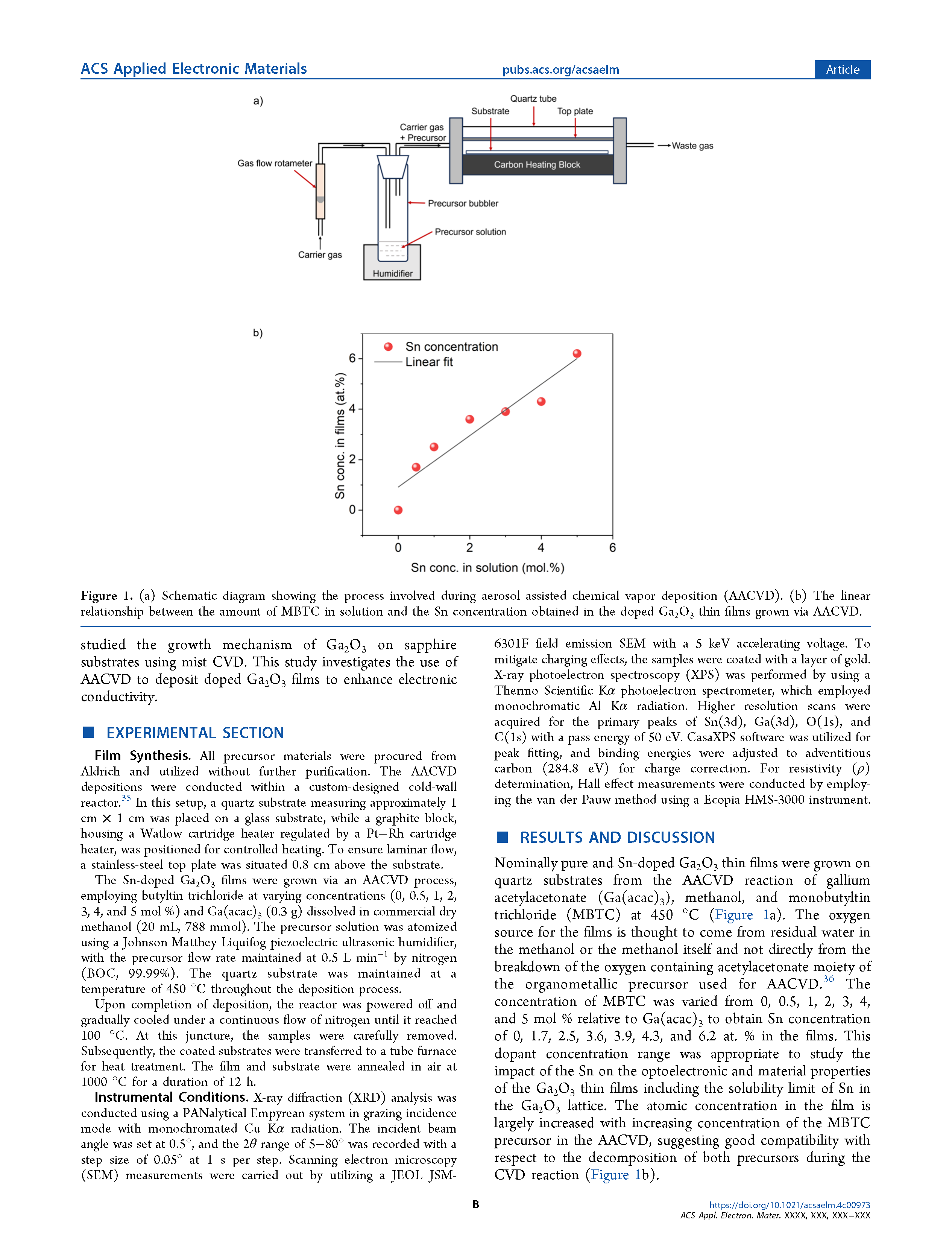
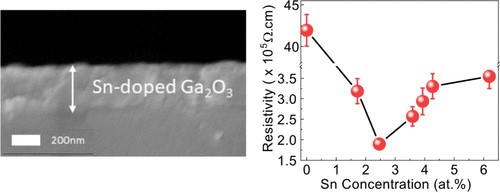
Figure 1. (a) Schematic diagram showing the process involved during aerosol assisted chemical vapor deposition (AACVD). (b) The linear relationship between the amount of MBTC in solution and the Sn concentration obtained in the doped Ga2O3 thin films grown via AACVD.
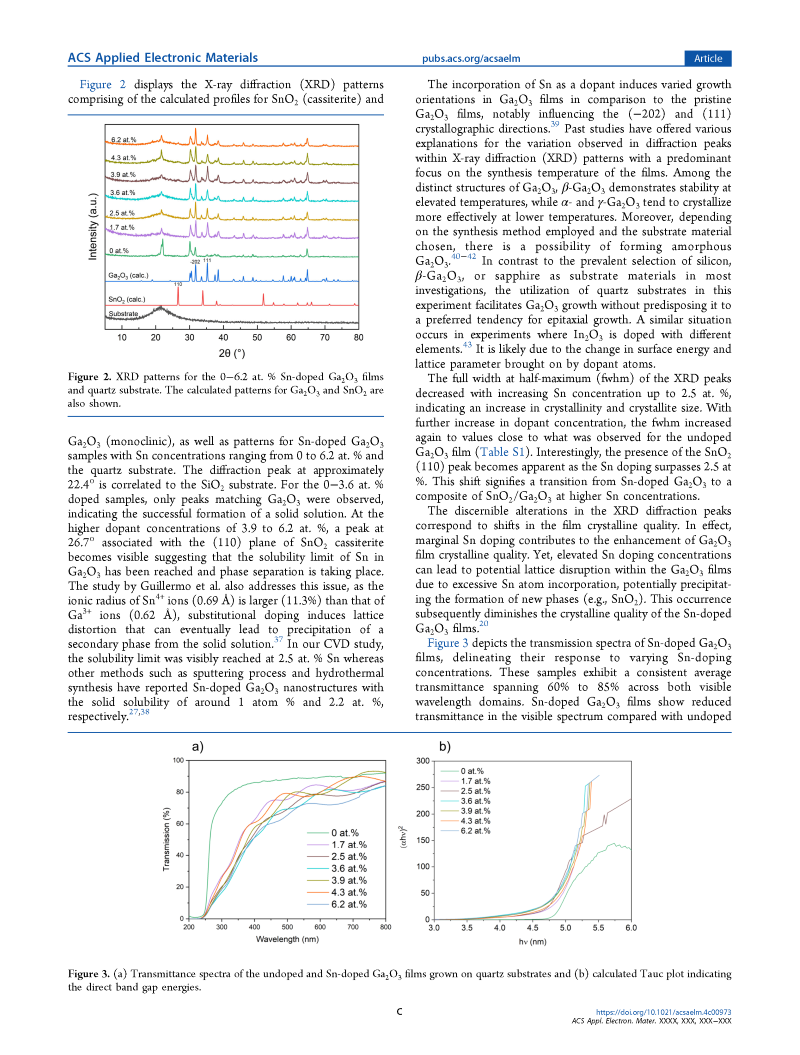
Figure 2. XRD patterns for the 0–6.2 at. % Sn-doped Ga2O3 films and quartz substrate. The calculated patterns for Ga2O3 and SnO2 are also shown.
DOI:
doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.4c00973