【Member Papers】Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications——Ultraviolet communication system utilizing effective performance β-Ga₂O₃ photodetector
日期:2024-12-19阅读:679
Researchers from the Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications have published a dissertation titled "Ultraviolet communication system utilizing effective performance β-Ga2O3 photodetector" in Applied Physics Letters.
Abstract
In recent years, solar-blind ultraviolet photodetectors (PDs) based on β-Ga2O3 have gained significant attention for their applications in military and commercial fields. This study explores the grain orientation and crystal quality of Ga2O3 films grown on sapphire substrates via RF magnetron sputtering at various growth temperatures and post-annealing temperatures. After determining optimal temperatures, we investigated the photoelectric performance of the metal/semiconductor/metal detectors with different oxygen flow ratios (0%, 5%, 10%). The PD grown in a pure Ar atmosphere exhibited the highest responsivity (48.93 A/W), remarkable detectivity (1.35 × 1014 Jones), excellent external quantum efficiency (2.39 × 104%), and also rapid photoresponse time (0.118 s rise time/0.031 s decay time) under 1000 μW/cm2 254 nm light illumination. These results are attributed to the internal gain from an optimal concentration of oxygen vacancies in the well-crystallized film, without the deep-level defects typically induced under oxygen-rich conditions. Leveraging this optimized chip, we developed a deep ultraviolet communication system using a Ga2O3-based detector. The system achieved a data rate of 65 kbps with a pseudo-random binary sequence signals utilizing on-off keying. Additionally, using discrete multi-tone signals modulated with 32-quadrature amplitude modulation, it reached a maximum data rate of 80.65 kbps, both satisfying forward error correction threshold of 3.8 × 10−3. These results highlight the considerable potential of high-quality β-Ga2O3 solar-blind PDs for ultraviolet communication applications.
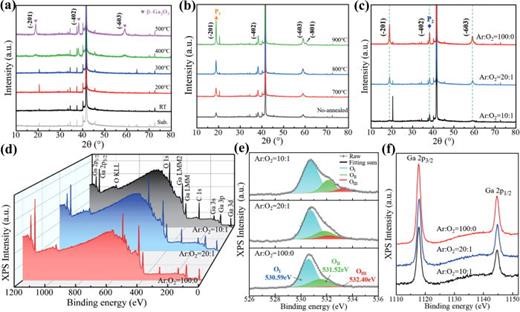
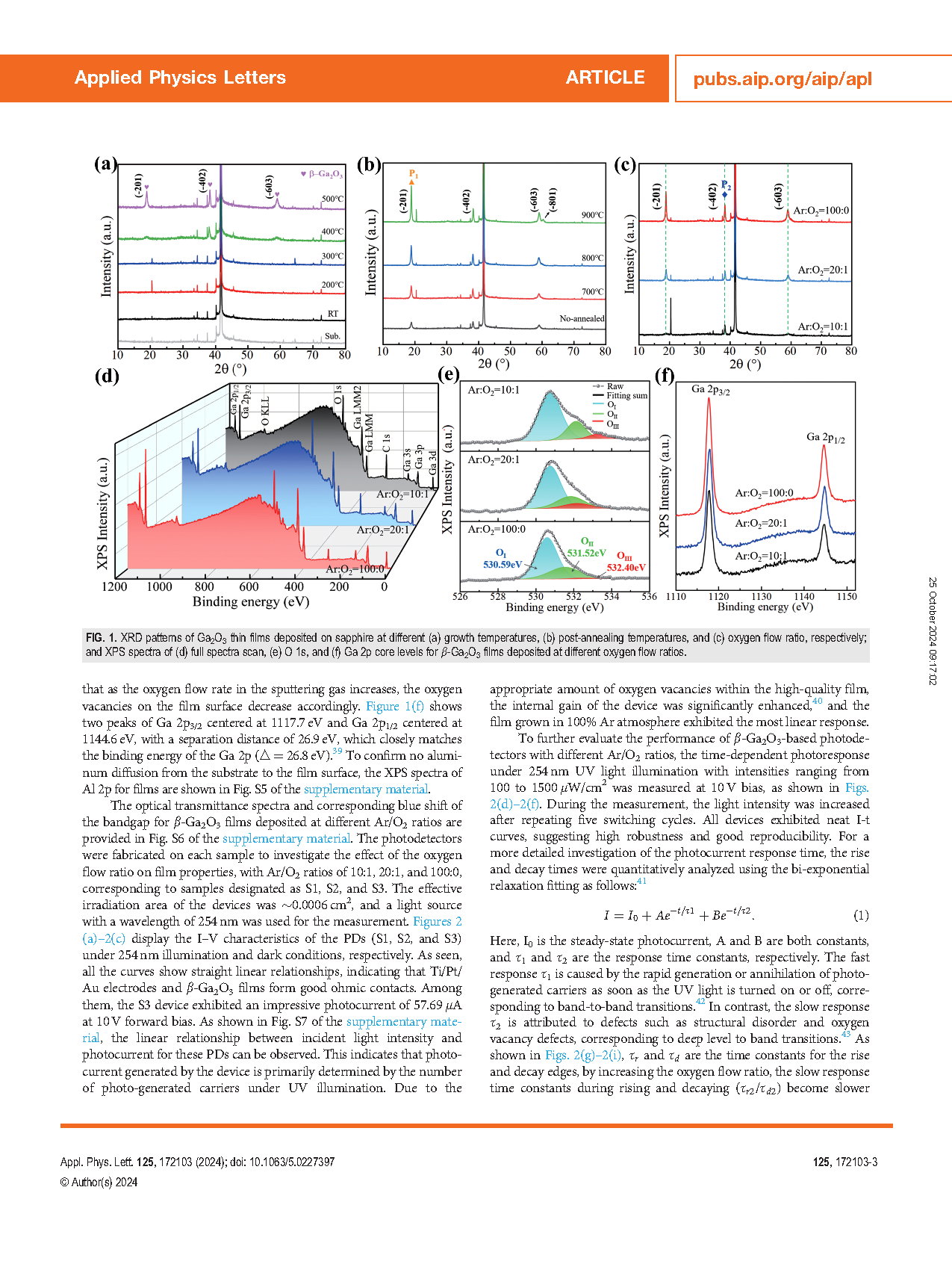
FIG. 1. XRD patterns of Ga2O3 thin films deposited on sapphire at different (a) growth temperatures, (b) post-annealing temperatures, and (c) oxygen flow ratio, respectively; and XPS spectra of (d) full spectra scan, (e) O 1s, and (f) Ga 2p core levels for β-Ga2O3 films deposited at different oxygen flow ratios.
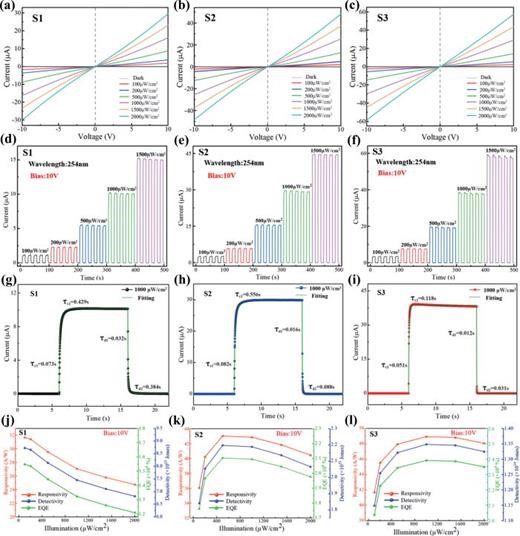
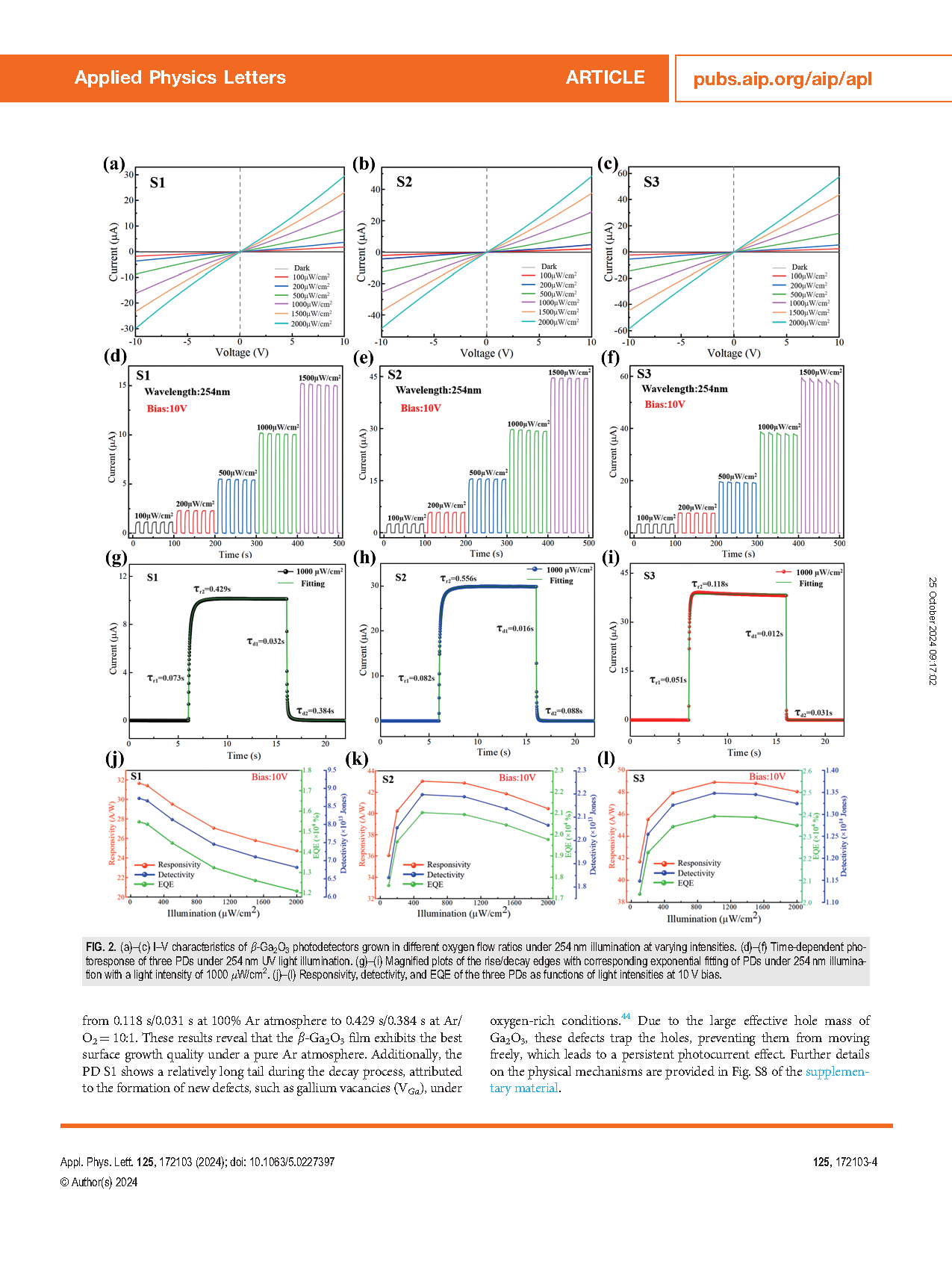
FIG. 2. (a)–(c) I–V characteristics of β-Ga2O3 photodetectors grown in different oxygen flow ratios under 254 nm illumination at varying intensities. (d)–(f) Time-dependent photoresponse of three PDs under 254 nm UV light illumination. (g)–(i) Magnified plots of the rise/decay edges with corresponding exponential fitting of PDs under 254 nm illumination with a light intensity of 1000 μW/cm2. (j)–(l) Responsivity, detectivity, and EQE of the three PDs as functions of light intensities at 10 V bias.
DOI:
doi.org/10.1063/5.0227397