【Domestic Papers】University of Chinese Academy of Sciences Explore——High Temperature Image Pre-Processing Based on ε-Ga₂O₃ Photo-Synapses
日期:2025-02-11阅读:572
Researchers from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences have published a dissertation titled "High Temperature Image Pre-Processing Based on ε-Ga2O3 Photo-Synapses" in Advanced Physics Research.
Abstract
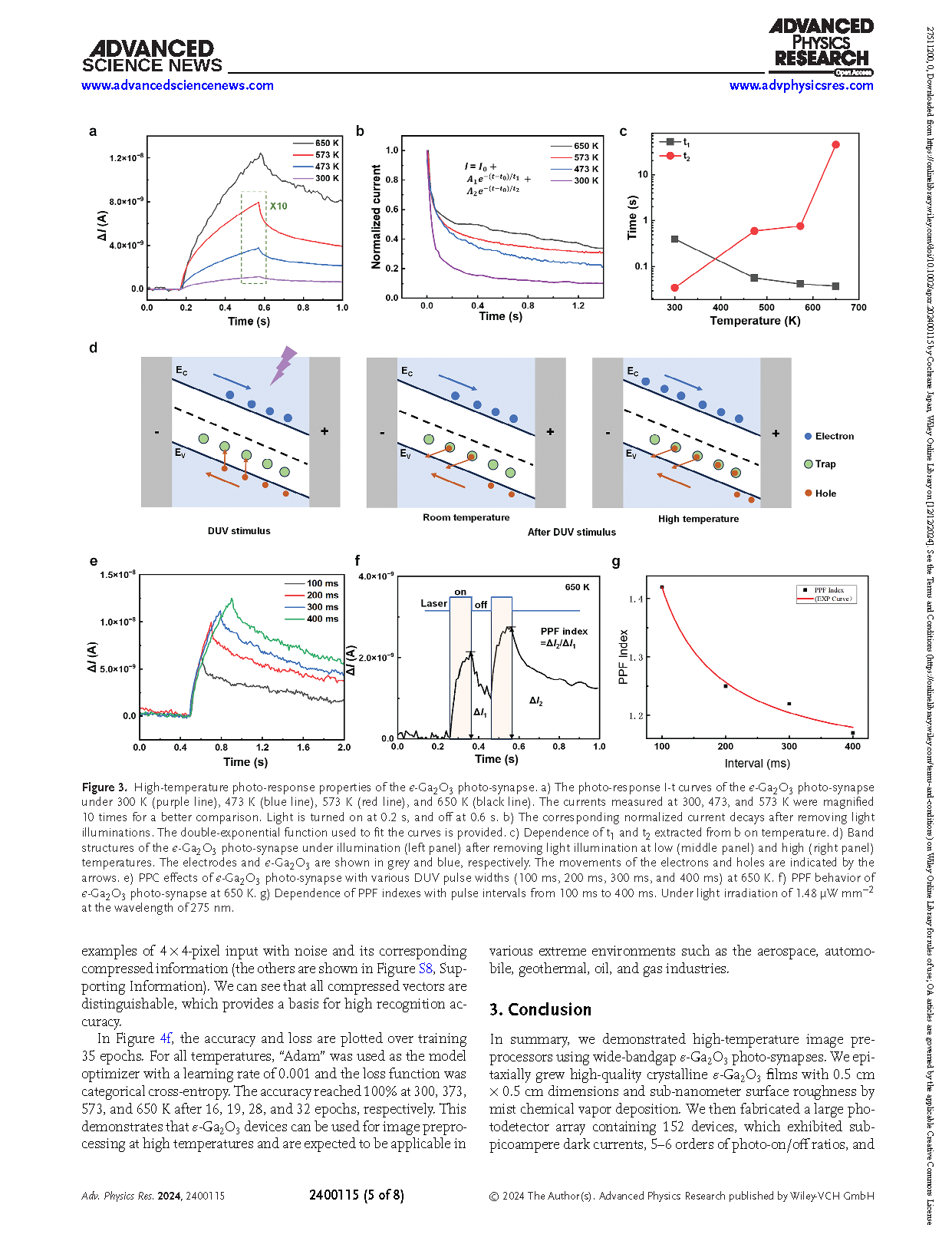
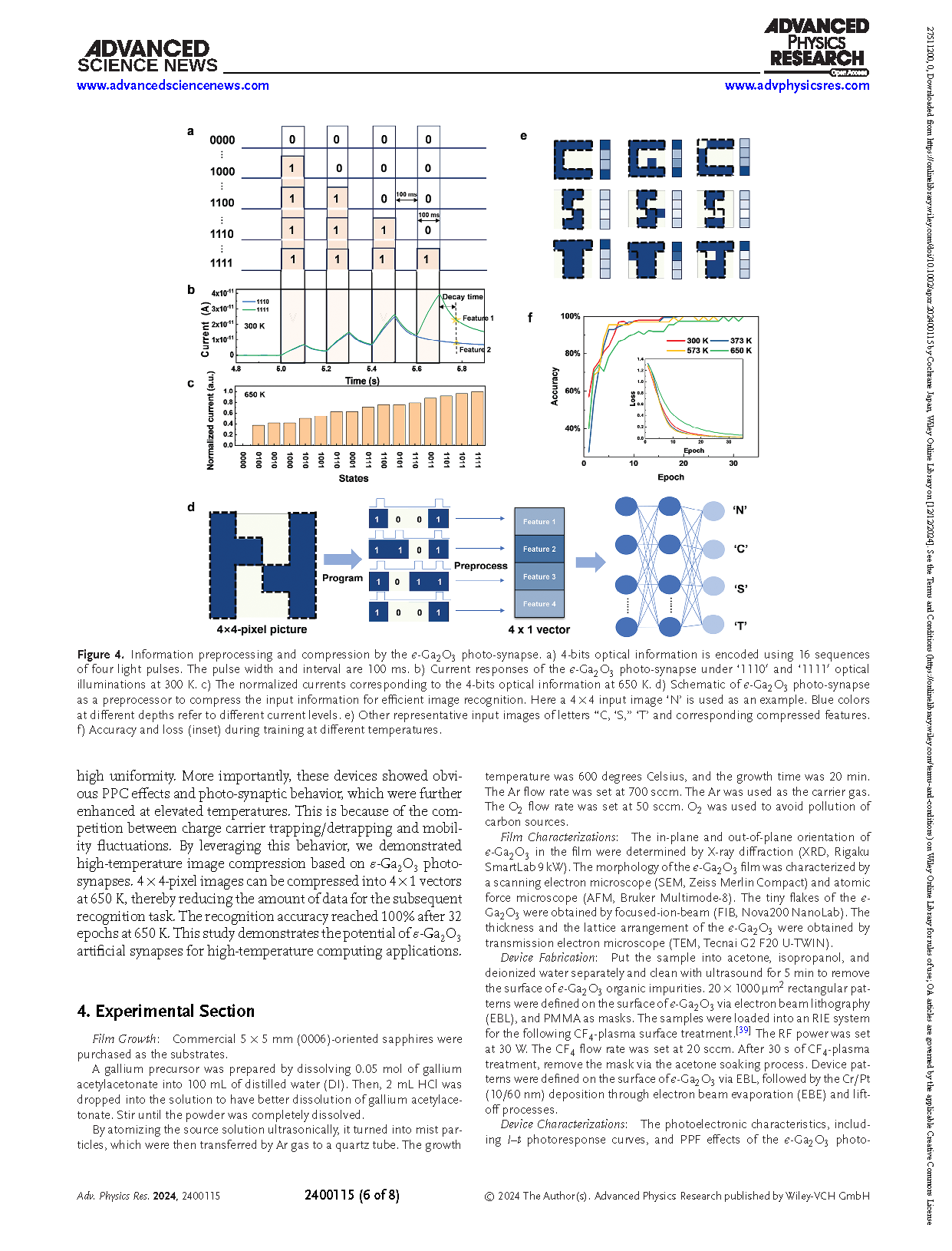
The era of big data has brought about substantial challenges in terms of power consumption and communication bandwidth. Edge-based neuromorphic computing with data pre-processing can help alleviate these burdens and enhance overall system efficiency. However, existing neuromorphic devices are typically limited to operation at room temperature, restricting their applications in extreme environments. Here, the use of wide-bandgap ε-Ga2O3 photo-synapses as image pre-processors is demonstrated, even at temperatures as high as 650 K. This is possible because of the high-quality ε-Ga2O3 epitaxial films, which exhibit angstrom-level surface roughness, as evidenced by the highly uniform 152 photodetector devices. These devices show enhanced photo-synaptic behavior at elevated temperatures, enabling high-temperature image compression capability. The 4 × 4-pixel images are compresed into 4 × 1 vectors, achieving an image recognition accuracy of 100% at 650 K. This work demonstrates the potential of ε-Ga2O3 artificial synapses for extremely high-temperature computing.
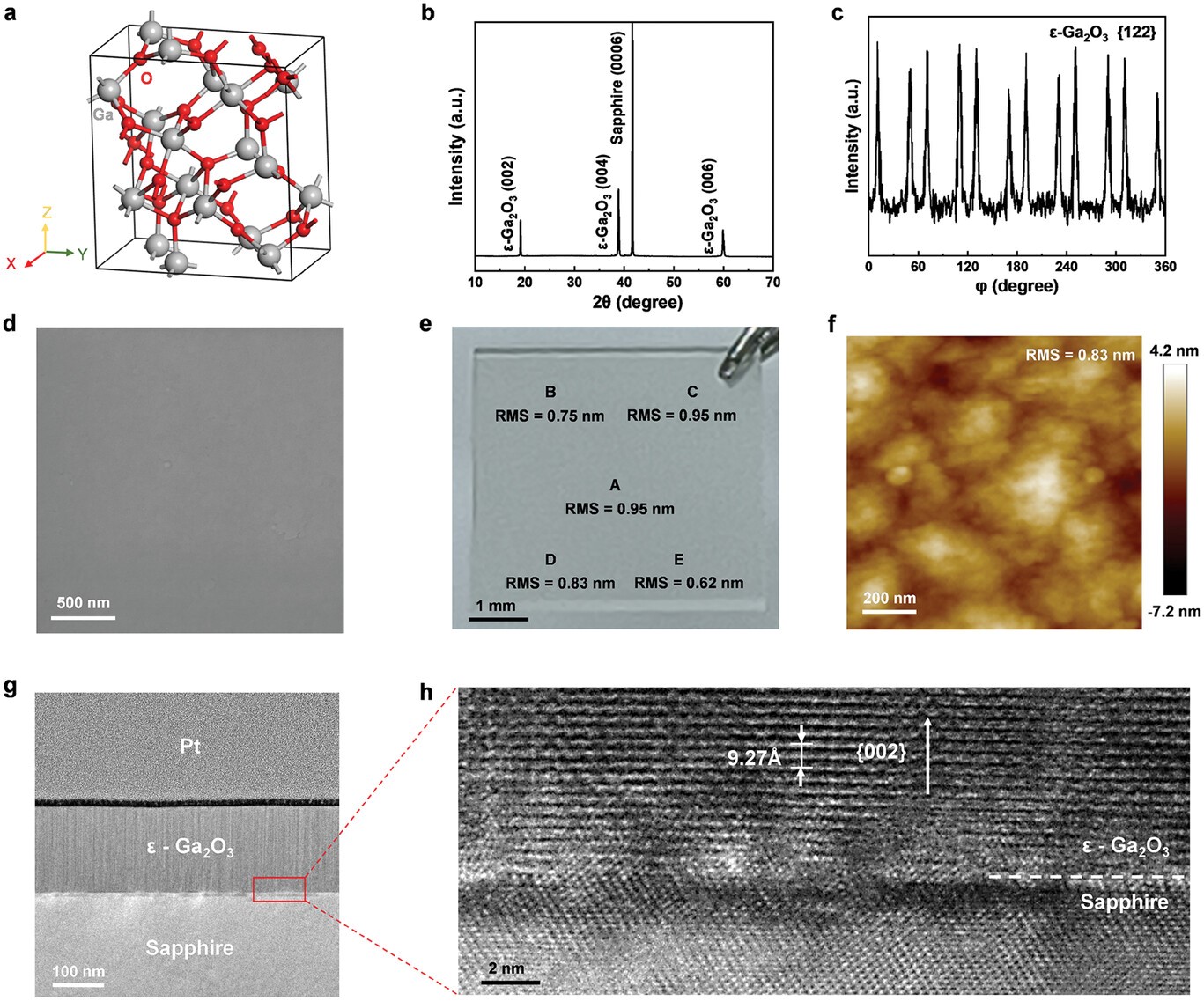
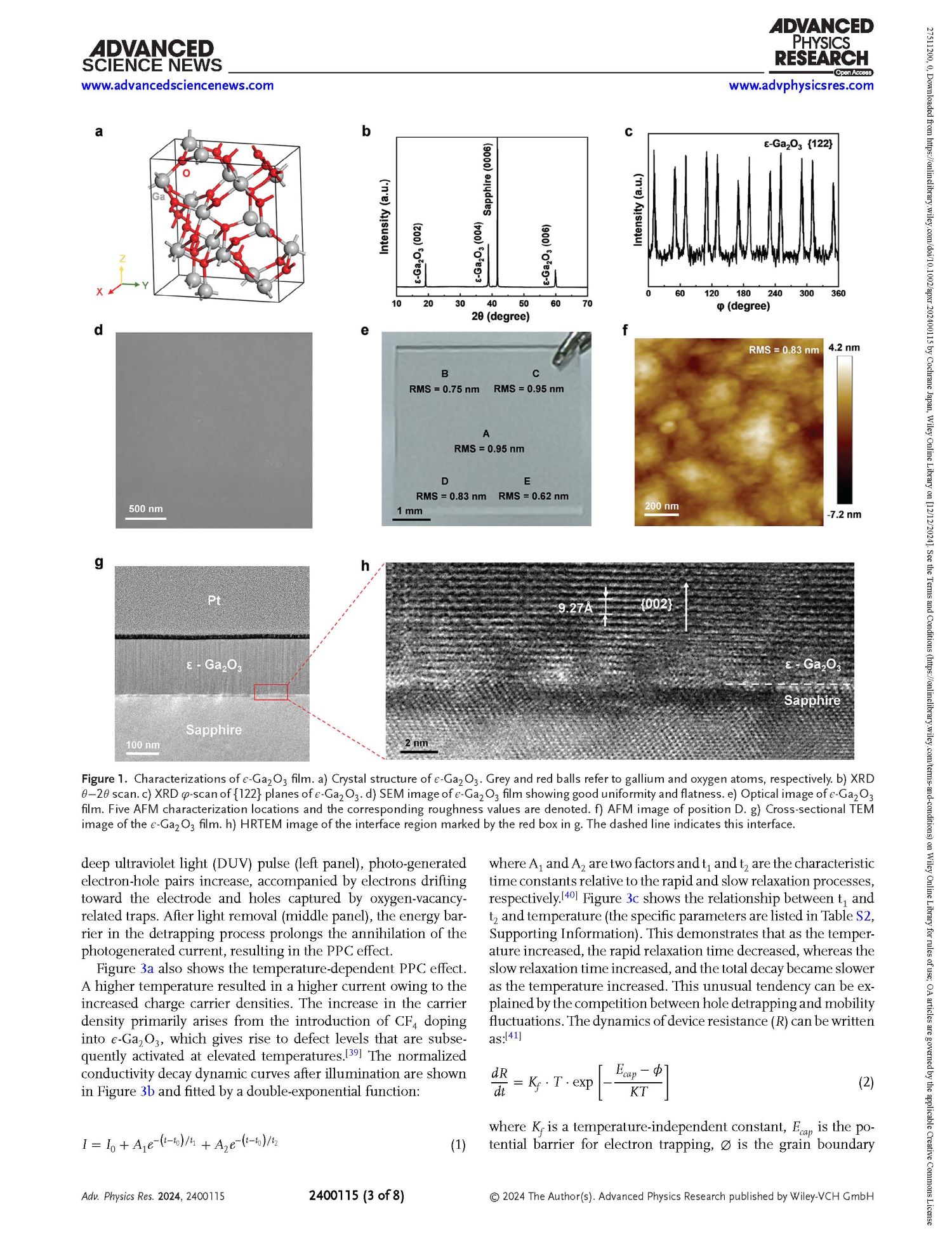
Figure 1 Characterizations of ε-Ga2O3 film. a) Crystal structure of ε-Ga2O3. Grey and red balls refer to gallium and oxygen atoms, respectively. b) XRD θ−2θ scan. c) XRD φ-scan of {122} planes of ε-Ga2O3. d) SEM image of ε-Ga2O3 film showing good uniformity and flatness. e) Optical image of ε-Ga2O3 film. Five AFM characterization locations and the corresponding roughness values are denoted. f) AFM image of position D. g) Cross-sectional TEM image of the ε-Ga2O3 film. h) HRTEM image of the interface region marked by the red box in g. The dashed line indicates this interface.
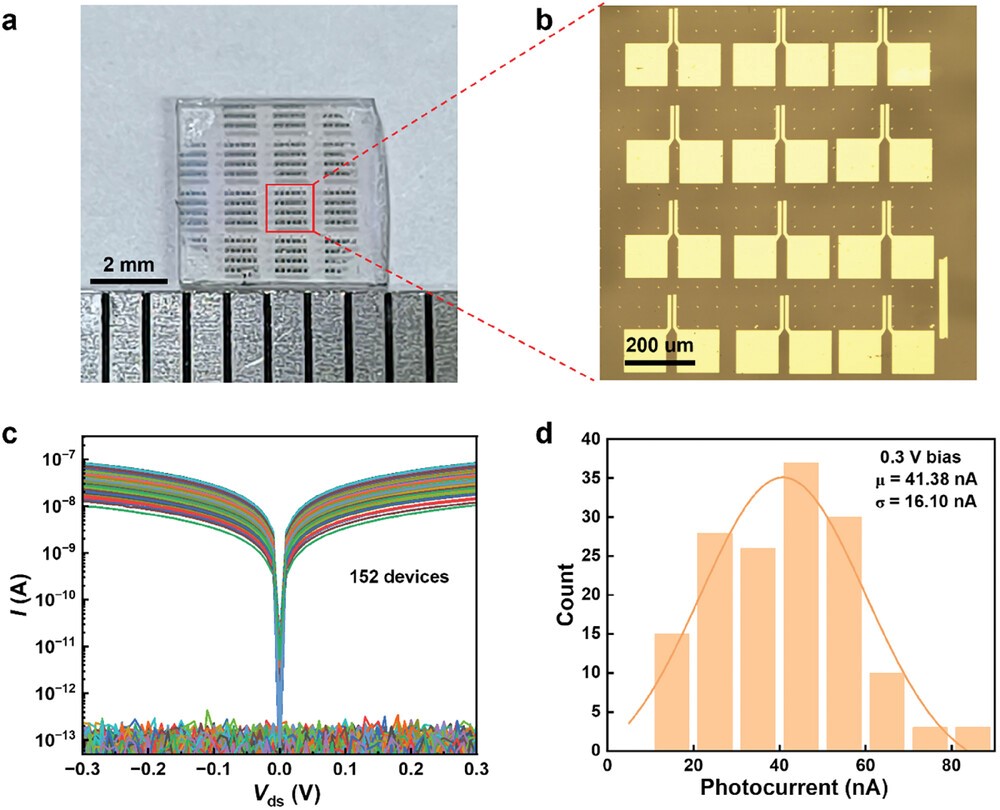
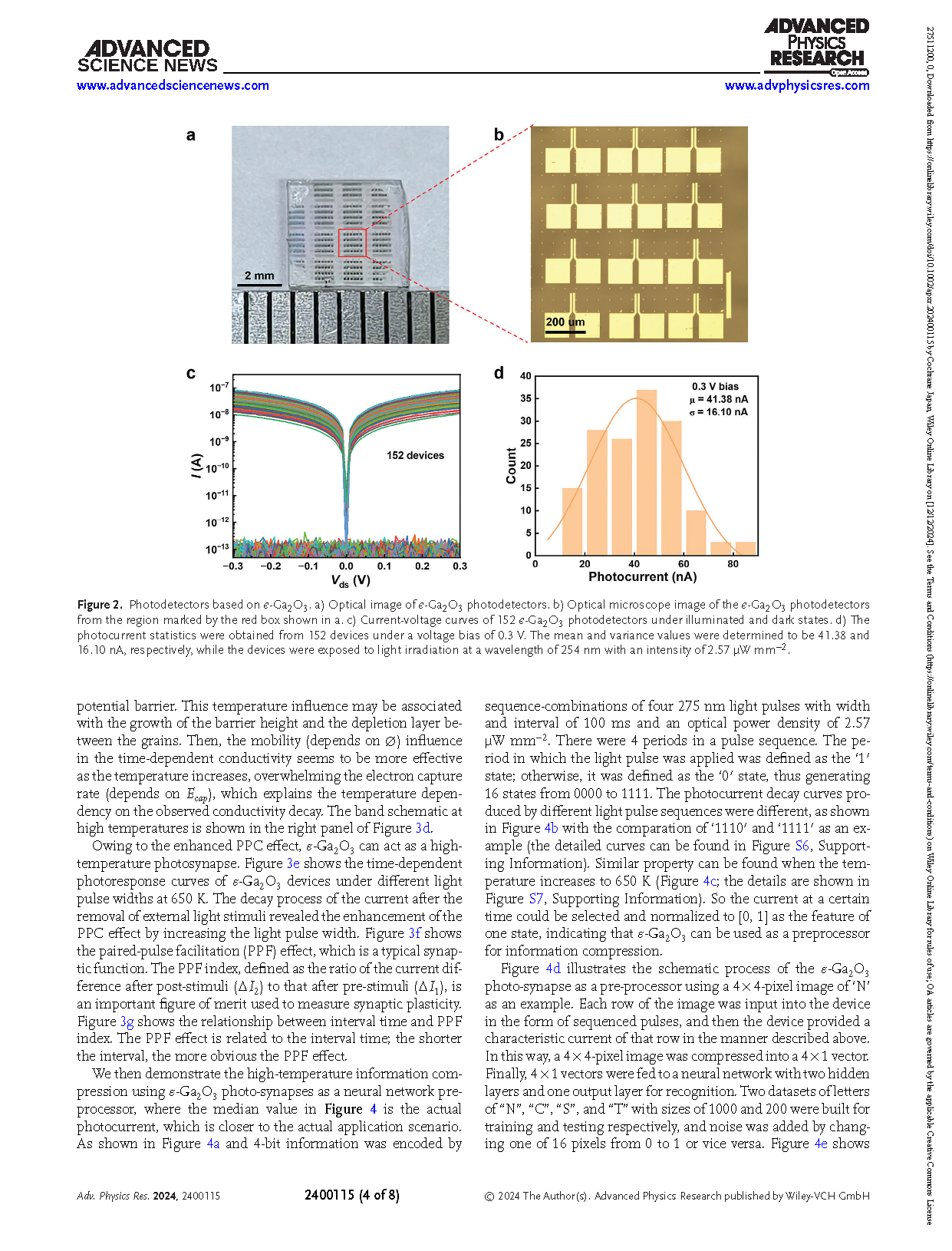
Figure 2 Photodetectors based on ε-Ga2O3. a) Optical image of ε-Ga2O3 photodetectors. b) Optical microscope image of the ε-Ga2O3 photodetectors from the region marked by the red box shown in a. c) Current-voltage curves of 152 ε-Ga2O3 photodetectors under illuminated and dark states. d) The photocurrent statistics were obtained from 152 devices under a voltage bias of 0.3 V. The mean and variance values were determined to be 41.38 and 16.10 nA, respectively, while the devices were exposed to light irradiation at a wavelength of 254 nm with an intensity of 2.57 µW mm−2.
DOI:
doi.org/10.1002/apxr.202400115