

【Domestic Papers】Alleviating trade-off between responsivity and response speed of Ga₂O₃ solar-blind photodetector via modulation of carrier redistribution and extraction accessibility
日期:2025-04-09阅读:532
Recently, the team of Long Shibing and Hu Qin of USTC College has made new progress in the research of solar-blind ultraviolet photodetection. Aiming at the mutual restriction of responsiveness and response speed in Gallium Oxide photodetectors, this research group innovatively proposed a design strategy of high-performance photodetectors based on Gallium Oxide double-layer thin film structure from theoretical and simulation analysis. The structure can alleviate the mutual restriction between responsiveness and response speed by regulating the internal electric field distribution and photo-generated carrier extraction path. Based on this design, a Gallium Oxide solar-blind UV photodetector with both high responsiveness and fast response speed is successfully constructed in this work, which verifies the effectiveness of this structure and its application potential in the field of Gallium Oxide solar-blind UV photodetection. This work provides a new idea for the further development of high-performance Gallium Oxide solar-blind photodetectors. The relevant results are entitled " Alleviating trade-off between responsivity and response speed of Ga2O3 solar-blind photodetector via modulation of carrier redistribution and extraction accessibility "was published in InfoMat, an internationally renowned academic journal.
Due to strong absorption by the atmosphere, the solar-blind part (ranging from 200 to 280 nm) in sunlight rarely reaches the surface of the earth, which empowers solar-blind photodetectors with the capacity for high anti-interference, high photosensitivity, and high reliability. Hence, solar-blind photodetectors have drawn extensive attention for versatile applications, such as environmental monitoring, solar-blind imaging, flame detection, photo communication, biomedical application, and aerospace application. At present, most commercial solar-blind UV photodetectors are based on silicon materials, but due to the wide absorption band of silicon materials and the low quantum efficiency in the solar-blind band, Silicon based solar-blind UV detectors face the problems of filter dependence and low responsiveness. Gallium Oxide materials have the advantages of solar-blind ultraviolet band, high photoelectric sensitivity, strong stability and low manufacturing cost, and have great potential in the field of solar-blind ultraviolet photodetector. However, at present, Gallium Oxide solar-blind photodetectors still face the problem of mutual restriction between high responsiveness and fast response speed, especially its slow response speed is far from the requirements of commercial application.
To address the above problems, this work innovatively proposes a high-performance detector design strategy based on a double-layer Gallium Oxide thin film structure (FIG. 1) based on theoretical and simulation analysis. The structure consists of a Gallium Oxide thin film Layer 1 with high responsiveness at the bottom Layer and a fast response speed at the upper layer Layer 2. The structure regulates carrier redistribution, electric field distribution and carrier extraction path within the Gallium Oxide film, so that the detector based on the structure combines the dual advantages of Layer 1 and Layer 2 (high responsiveness + fast response speed).
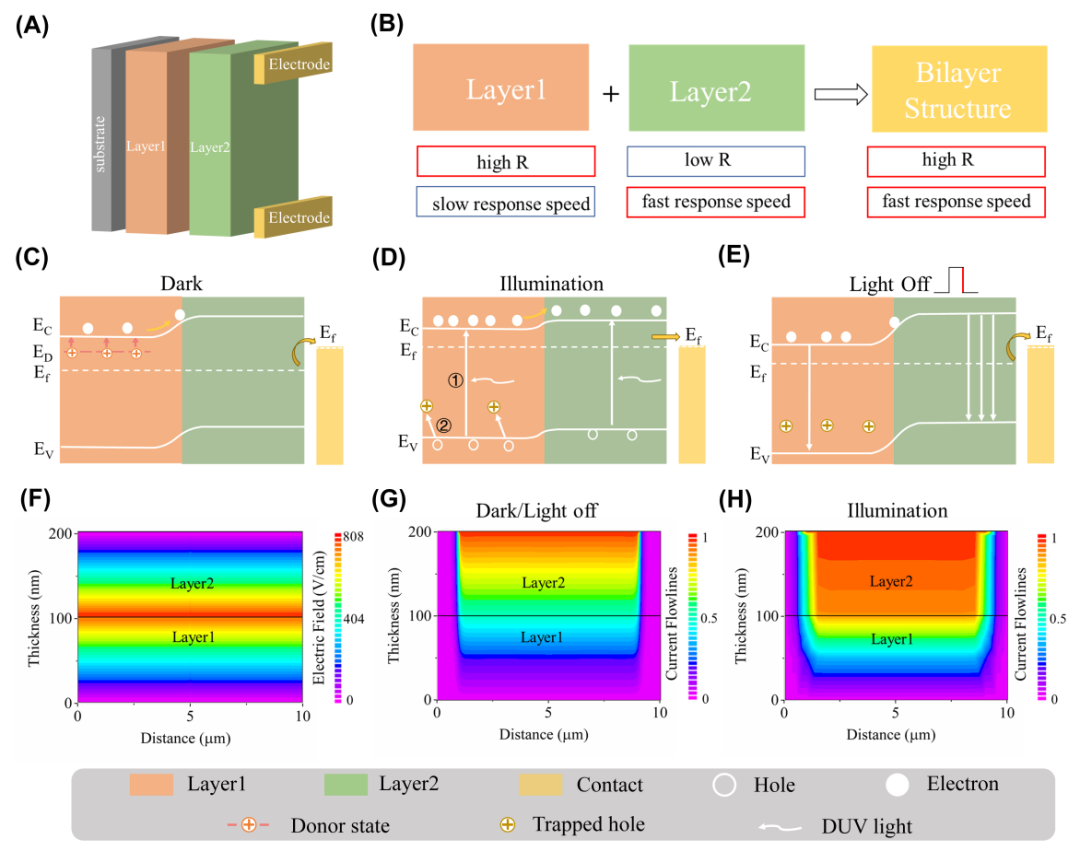
FIG. 1 Design diagrams of bilayer-structure Ga2O3 photodetector adopted in this work and the corresponding work mechanisms. Diagram of (A) bilayer-structure device and (B) the expected performance improvement effect. Diagram of energy band and photogenerated carriers dynamic process of bilayer-structure film (C) under dark, (D) illumination and (E) light off. (F) Simulated electric field distribution between the two Ga2O3 layers and simulated current flowlines distribution in bilayer-structure device under (G) dark/light off and (H) illumination condition.
Based on the above design, a Gallium Oxide solar-blind UV photodetector with both high responsiveness and high response speed is successfully realized in this work (FIG. 2). The optimized device achieves responsiveness up to 236.1 A/W and response speeds as low as 50 ms. In summary, this work proposes an innovative double-layer Gallium Oxide thin film structure design, and constructs high-performance Gallium Oxide solar-blind photodetector based on this design, successfully alleviates the mutual restriction between high responsiveness and high response speed, and also provides an effective scheme for the development of high-performance Gallium Oxide solar-blind photodetector.
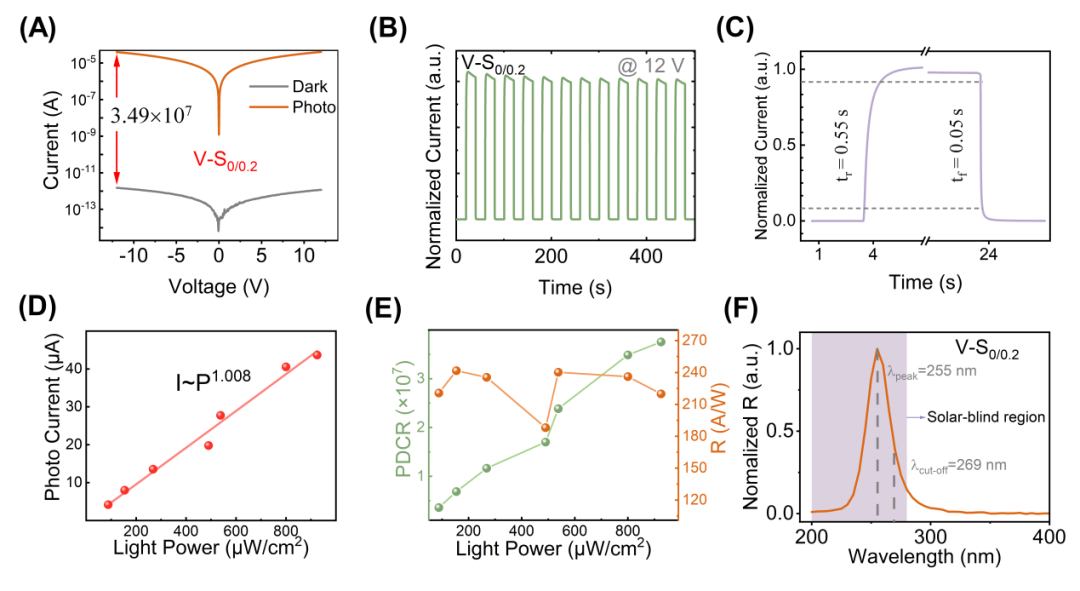
FIG. 2 Photoelectric response performance of devices based on double-layer Gallium Oxide thin film structure. (a)I-V response; (b) periodic I-T response; (c) a typical I-T response period; (D) the change of photocurrent with optical power; (E) the change of photodark current ratio (PDCR) and responsiveness (R) with optical power; And (F) normalization of the response spectrum.
This research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program and the Foundation of the University of Science and Technology of China, as well as by the Center for Micro and Nano Research and Manufacturing and the Center for Physical and Chemical Experiments of the University of Science and Technology of China. Hu Qin, Gao Nan and Hou Xiaohu are co-corresponding authors of the paper. Graduate students Ma Xiaolan and Dr. Tan Pengju and Zhang Ying are co-first authors of the paper. Prof. Long Shibing, Prof. Zhao Xiaolong and Prof. Xu Guangwei participated in the joint technical research of the project.
Links: {http://doi.org/10.1002/inf2.70016}


