【Member Papers】Southern University of Science---Enhancement-mode β-Ga₂O₃ MOSFETs and monolithic integrated inverters based on charge trapping layer technology
日期:2025-06-20阅读:335
Researchers from the Southern University of Science have published a dissertation titled "Enhancement-mode β-Ga₂O₃ MOSFETs and monolithic integrated inverters based on charge trapping layer technology" in ISPSD 2025.
Project Support
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission.
Background
β-Ga₂O₃ MOSFETs have shown significant potential for high-voltage, high-power applications owing to its high breakdown electric field (8 MV/cm) and wide bandgap (4.8 eV). To minimize parasitic inductance between the device and peripheral circuitry, enhance circuit stability, and reduce power consumption, β-Ga₂O₃-based integrated circuits have been proposed for the development of energy-efficient, high-density ICs and systems. However, the lack of effective p-type doping remains a major barrier to the development of CMOS logic circuits based on β-Ga₂O₃. As an alternative, direct-coupled field-effect transistor logic (DCFL) using n-channel enhancement-/depletion-mode (E/D-mode) devices provides a promising approach for realizing β-Ga₂O₃ integrated circuits. While previous studies have demonstrated DCFL inverters on sapphire substrates, research on monolithic integration of β-Ga₂O₃ devices is still limited.
Abstract
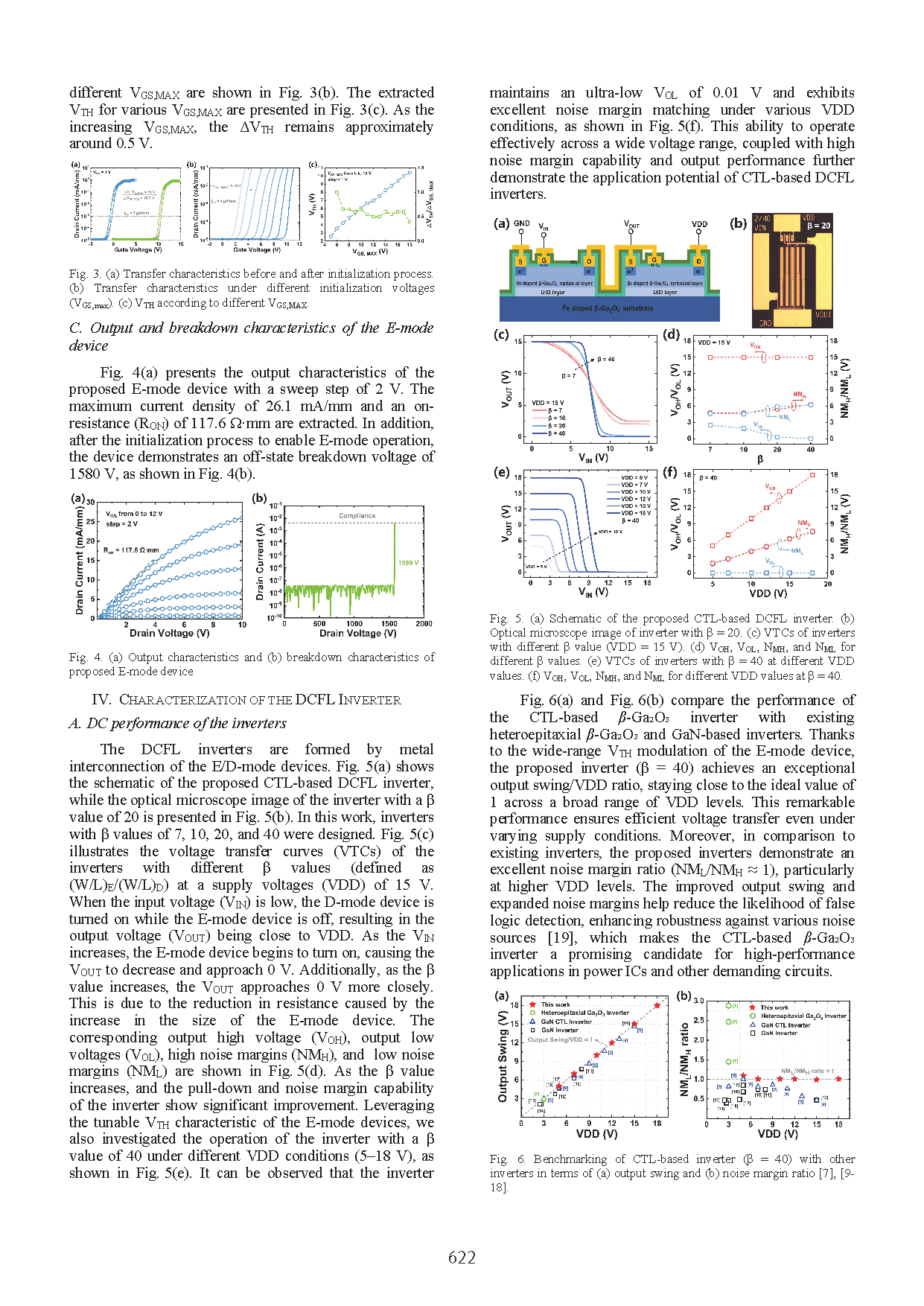
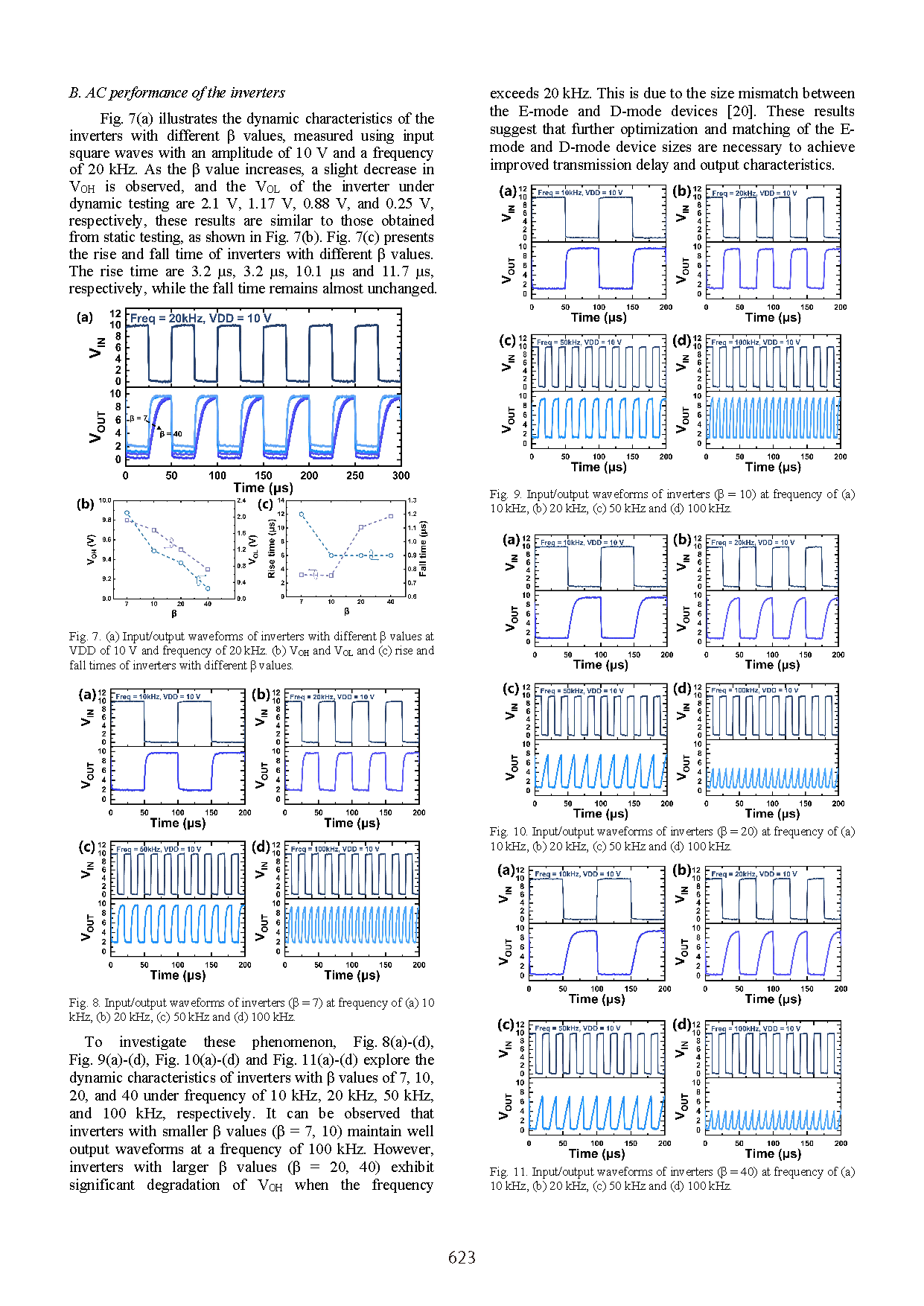
The research team proposed enhancement-mode (E-mode) MOSFETs based on a charge trapping layer (CTL) structure. By applying different initialization voltages to the gate, wide-range modulation of the threshold voltage (VTH) can be achieved, while avoiding channel damage typically caused by etching processes. The fabricated E-mode devices exhibited a VTH tunability of up to 10.9 V. Leveraging this tunable VTH characteristic, the proposed CTL-based inverters are capable of stable operation under supply voltages (VDD) ranging from 5 to 18 V. In particular, the inverter with a β value ((WG/LG)E/(WG/LG)D) of 40 demonstrated an ultra-low output low level (VOL = 0.01 V), an excellent output swing ratio (17.99 V/18 V), and an outstanding noise margin ratio (NML/NMH = 7.65 V/7.55 V @ VDD = 18 V). Furthermore, dynamic tests were carried out to evaluate the performance of devices with different β values at various frequencies. These results present a viable technological pathway for the fabrication of β-Ga₂O₃ integrated circuits.
Conclusion
This work developed a monolithic integrated β-Ga₂O₃ inverter based on CTL technique, enabling the realization of homoepitaxial monolithic integrated β-Ga₂O₃ devices. Benefiting from the wide tunability of the threshold voltage in the E-mode device, the CTL-based inverter demonstrated excellent matching across different VDD values (5–18 V). Moreover, by adjusting the device size ratio, significant improvements were achieved in the pull-down strength, output swing, and noise margin of the inverter. Furthermore, the dynamic characteristics of inverters with different β values at various frequencies indicate that proper E/D-mode device size matching can effectively reduce parasitic parameters, thereby reducing power consumption and enabling higher-frequency applications. These findings present a promising approach for realizing the β-Ga₂O₃ power IC platforms.
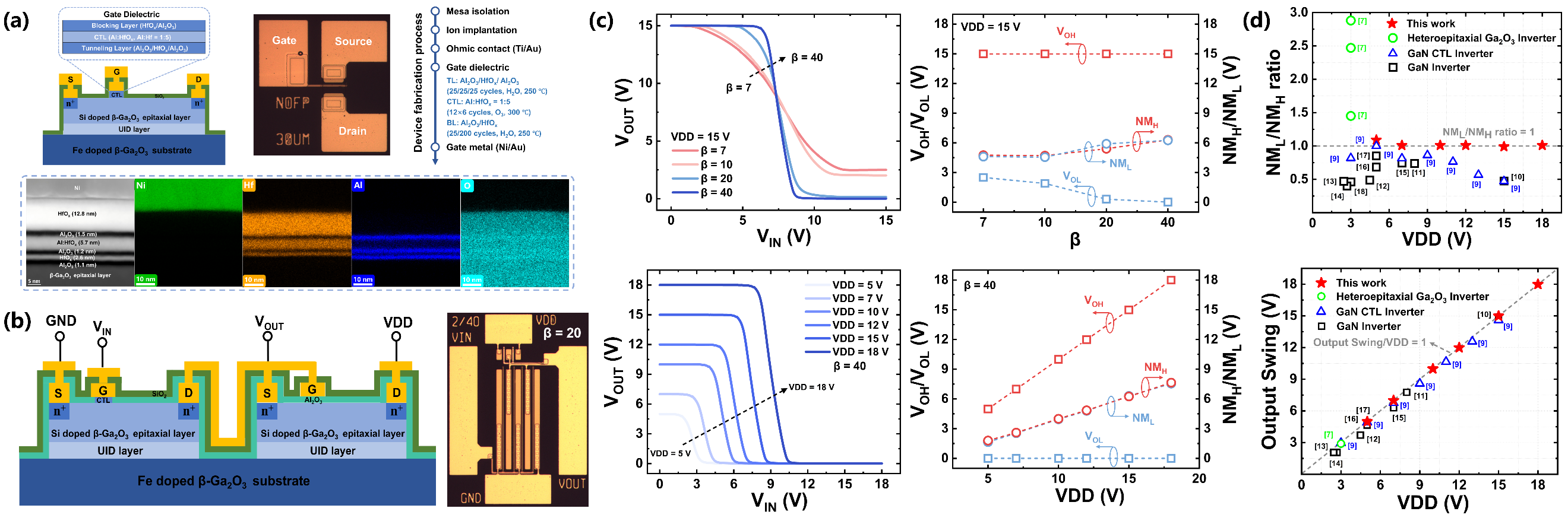
Figure 1. (a) Cross-sectional schematic of the E-mode device, optical microscope image of the device, fabrication process flow, and TEM/EDS characterization of the gate dielectric. (b) Cross-sectional schematic of the monolithically integrated inverter and optical microscope image of the inverter. (c) Voltage transfer characteristics (VTCs) of inverters with different β values at VDD = 15 V, and VTCs of the β= 40 inverter under various VDD values, along with the corresponding VOH, VOL, NMH, and NML values. (d) Benchmark plots of inverter noise margin and output swing.