

【Member News】Breaking Through the “Blind” Zone, Envisioning the Future: Industrialization of Gallium Oxide–Based Solar-Blind UV Photodetector Chips
日期:2025-10-24阅读:467
Recently, a research team from Tianjin University of Technology, in collaboration with Tianjin Infray Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd., launched the first gallium oxide–based solar-blind ultraviolet (UV) photodetector chip. This chip exhibits a specific response to light with a wavelength of 260 nm, achieving a photo-to-dark current ratio of 5.5×10⁵ under a −10 V bias, fully meeting the application requirements for photodetector chips. The team has established independent and controllable full-chain technology, spanning from epitaxial material growth and chip design and fabrication to packaging and testing. The chip is currently undergoing application verification.
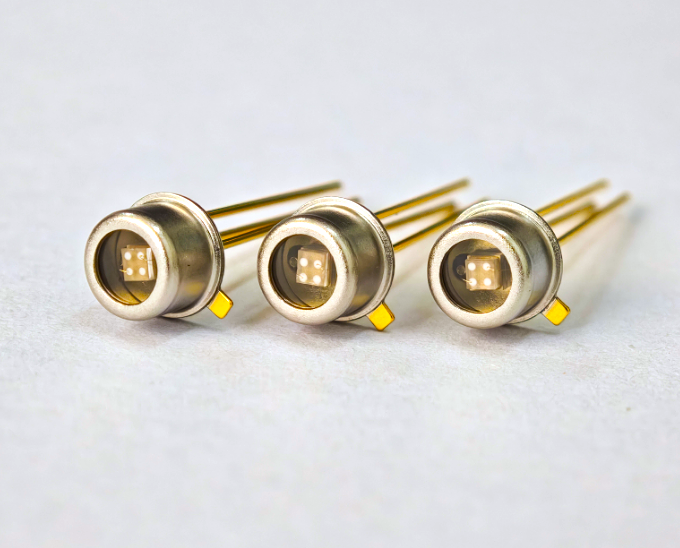

Figure 1. Gallium Oxide–based solar-blind ultraviolet photodetector
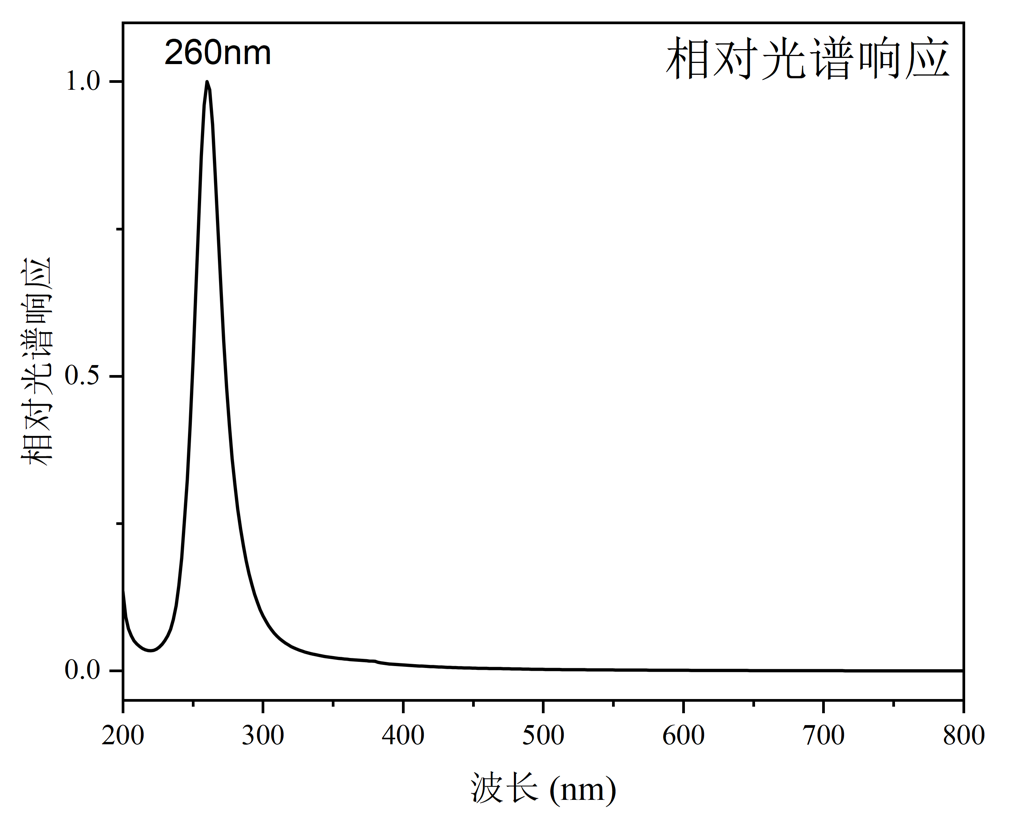
Figure 2. Spectral response curve of the gallium oxide solar-blind UV photodetector chip
Solar-blind UV detection technology refers to the detection of ultraviolet radiation in the 200–280 nm wavelength range, which is strongly absorbed by the ozone layer and thus cannot reach the Earth's surface. Since this spectral range is almost “dark” in natural sunlight, any artificial radiation within it can be easily distinguished, resulting in extremely high signal-to-noise ratios and very low false alarm rates.
The photosensitive region of the product adopts a self-developed Gallium Oxide epitaxial layer. As a representative ultra-wide-bandgap semiconductor material, gallium oxide possesses a bandgap as wide as 4.9 eV, making it naturally sensitive to solar-blind UV light while being completely insensitive to visible light. This makes Ga₂O₃ the ideal material for solar-blind UV photodetectors. Compared with traditional solutions, Gallium Oxide–based detectors achieve high wavelength selectivity without the need for expensive optical filters, offering disruptive advantages in performance, cost, and compactness.
The industrialization of gallium oxide solar-blind UV photodetectors holds broad application prospects in power safety monitoring, forest fire prevention and firefighting, defense and missile early warning, environmental and scientific exploration, and industrial process control.
Tianjin Infray Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd. is a company specializing in gallium-based semiconductor optoelectronic detection chips, engaged in design, production, and sales of optoelectronic chips. Its core business focuses on optoelectronic chips and intelligent equipment. The company’s chip products include broad-spectrum gas detection chips, avalanche photodiodes (APDs), high-frequency and high-speed photodetectors, high-power DFB lasers, and single-photon detectors, which are widely used in environmental monitoring, optical communications, medical imaging, industrial inspection, radar, quantum communication, and defense applications.
Its equipment portfolio covers SWIR industrial cameras, AI spectrometers, OCT medical imaging systems, and high-power laser equipment for UAVs and low-altitude reconnaissance. The company has achieved several key technological breakthroughs, including nanostress regulation for ultra-broadband detection, facet passivation to extend laser chip lifetime and yield, and independently developed high-power DFB and low-dark-current single-photon detector chips—some of which have reached or even surpassed international performance benchmarks.
By 2024, Infray Semiconductor Technology’s chip shipments exceeded 3 million units, and equipment shipments surpassed 1,000 units, ranking among the top domestic suppliers in gas detection chips.
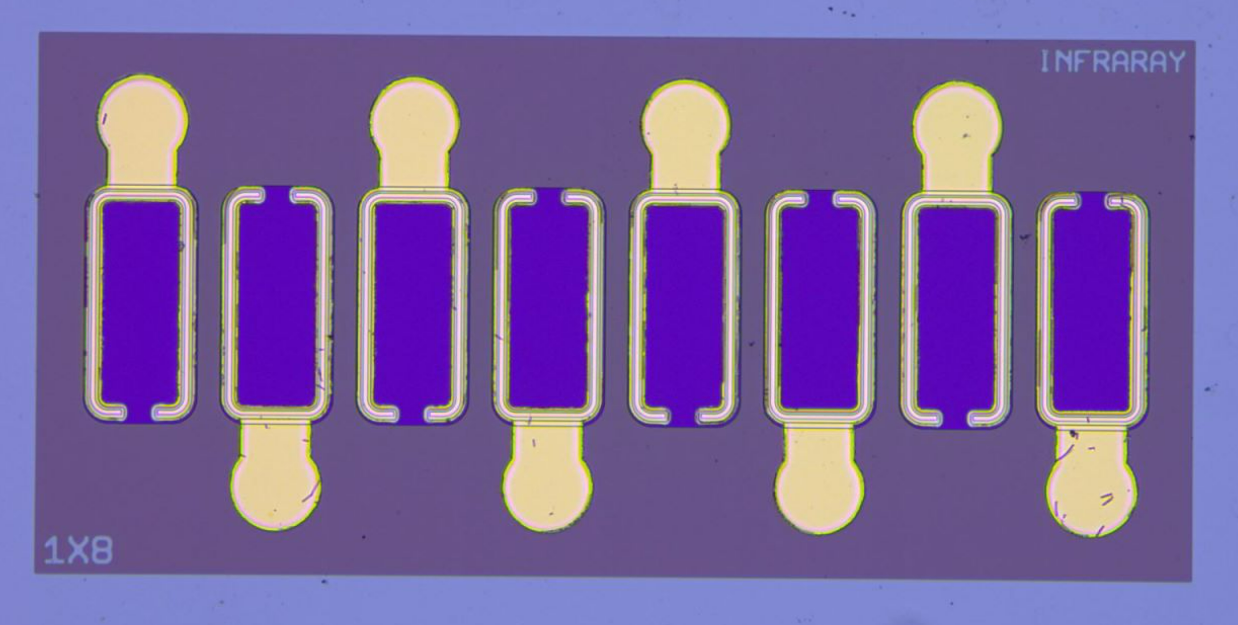
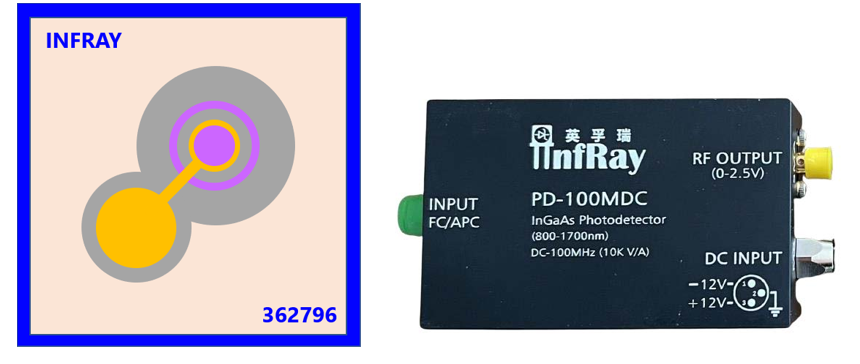
Figure 3. Selected mass-produced products by Infrared Semiconductor, including PIN-type linear array photodetectors, large-area linear APDs, and photodetector modules.


